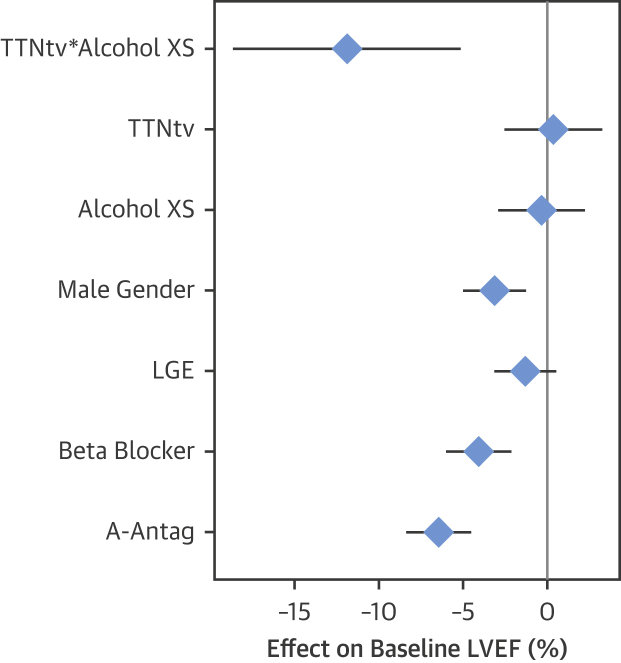
Figure 2.
Alcohol and TTNtv Act in Combination, and Together Are Associated With a Lower Baseline LVEF in Patients With DCM
Forest plot showing regression coefficient and 95% confidence intervals from the multivariable linear regression model evaluating the effects of TTNtv and excess alcohol consumption on baseline LVEF. The effect on LVEF is shown as absolute difference in LVEF (% = expressed as percentage of end-diastolic volume) between groups. A-Antag = aldosterone antagonist; Alcohol XS = excess alcohol consumption (binary variable indicating consumption >21 U/week for men, >14 U/week for women); LGE = late gadolinium enhancement (indicative of mid-wall fibrosis) on cardiovascular magnetic resonance; LVEF = left ventricular ejection fraction; TTNtv = presence of truncating variant in titin; TTNtv*Alcohol XS = interaction term representing individuals with both a TTNtv and a history of excess alcohol consumption.