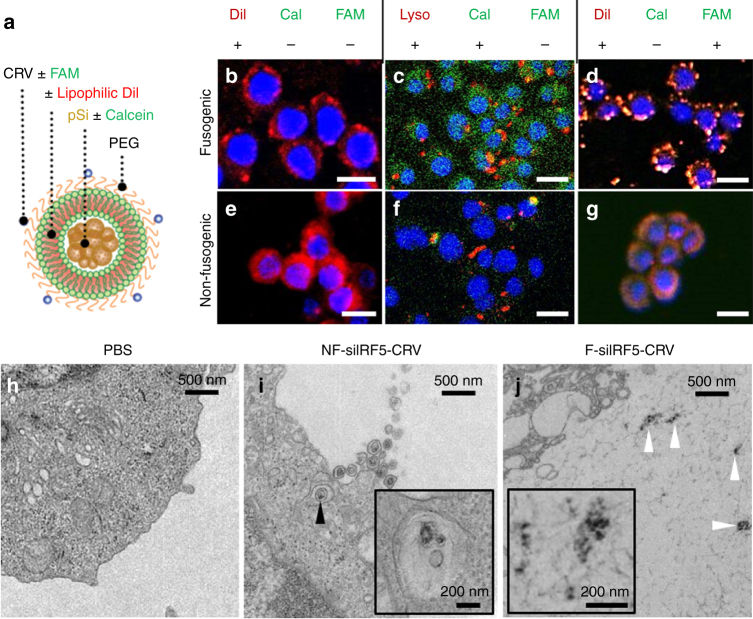
Fig. 2.
Fusion and intracellular delivery of Fusogenic particles in vitro. a Particle schematic. Calcein, anionic calcein fluorescent dye; CRV, macrophage-targeting peptide; DiI, the hydrophobic carbocyanine membrane stain; FAM, fluorescein label attached to targeting peptide; PEG, polyethylene glycol; pSi, porous Si nanoparticles. b–g Confocal microscope images of J771A.1 murine macrophage cells; b after 10 min incubation with DiI-loaded F-pSi nanoparticles; c after 1 h incubation with Lysotracker Red and 10 min incubation with calcein-loaded F-pSi nanoparticles; d after 5 min incubation with CRV-FAM-conjugated, DiI-loaded F-pSi nanoparticles; e after 10 min incubation with DiI-loaded NF-pSi nanoparticles; f after 1 h incubation with Lysotracker Red and 10 min incubation with calcein-loaded NF-pSi nanoparticles; g after 5 min incubation with CRV-FAM-conjugated, DiI-loaded NF-pSi nanoparticles. Blue is DAPI nuclear stain. h–j Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of Raw 264.7 murine macrophage cells after 10 min incubation with nanoparticles. h Cells treated with PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) control show no signs of particles; i cells treated with nanoparticles containing a non-fusogenic lipid coating, siRNA against transcription factor Irf5, and the macrophage-targeting peptide (NF-siIRF5-CRV) display evidence of pinocytotic uptake (arrowhead). Inset shows particles localized in vesicles (endosome/lysosome); j cells treated with nanoparticles containing fusogenic lipid coating, siRNA against transcription factor IRF5, and the macrophage-targeting peptide (F-siIRF5-CRV) become localized in the cell cytoplasm. Scale bar represents 20 µm