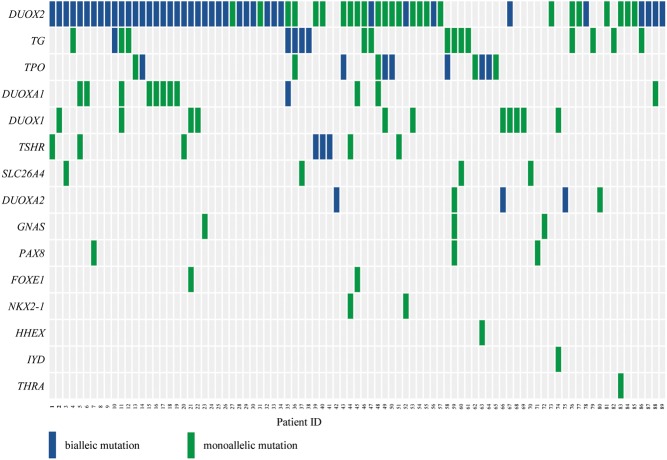
Figure 2.
Mutations detected in 89 patients with congenital hypothyroidism. The right side were the 15 mutated genes, the bottom were the patient ID. Each column represents one patient and each row represents one gene. Blue blocks represent biallelic mutations (containing compound heterozygous mutations and homozygous mutations) and green blocks represent monoallelic mutations (heterozygous mutation). For example, patient 4 carries mutations in two genes, biallelic mutations in the DUOX2 gene in addition to a monoallelic TG mutation. Patient 5 carries mutations in three genes, biallelic mutations in the DUOX2 gene and a monoallelic mutation in DUOXA1 in addition to a monoallelic TSHR mutation. A total of 57 patients carried biallelic mutations in DUOX2, TG, TPO, TSHR, DUOXA2 or DUOXA1. A total of 66 patients harbored mutations in DUOX2, which was the most frequently mutated gene.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a