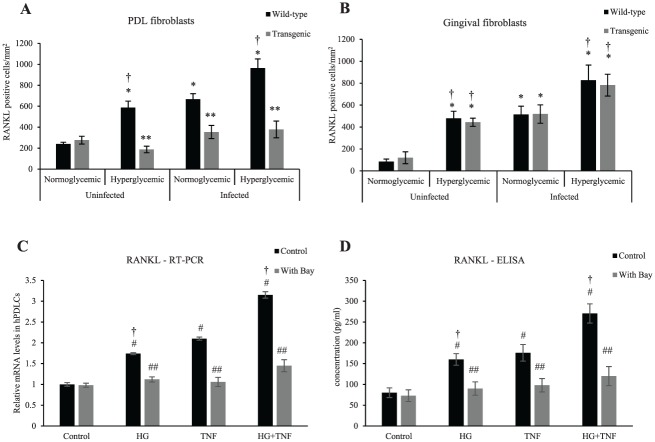
Figure 3.
Transgenic mice with lineage-specific inhibition of NF-κB have reduced RANKL expression in PDL fibroblasts not gingival fibroblasts. (A) RANKL expression by fibroblastic cells in the PDL was measured by immunofluorescence. (B) RANKL expression by gingival fibroblasts was measured by immunofluorescence. (C) RANKL mRNA levels were assessed by qRT-PCR when stimulated with high glucose and/or TNF-α with or without the NF-κB inhibitor BAY-117082. (D) RANKL protein levels in hPDLCs were measured by ELISA assay when stimulated with high glucose and/or TNF-α with or without BAY-117082 for 3 d. *P < 0.05 (vs. uninfected normoglycemic group). **P < 0.05 (vs. matched wild-type group). #P < 0.05 (vs. untreated control group). ##P < 0.05 (vs. matched control group). †P < 0.05 (vs. matched normoglycemic group). hPDLC, human periodontal ligament cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; PDL, periodontal ligament; RANKL, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; qRT-PCR, real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Error bars indicate SEM.