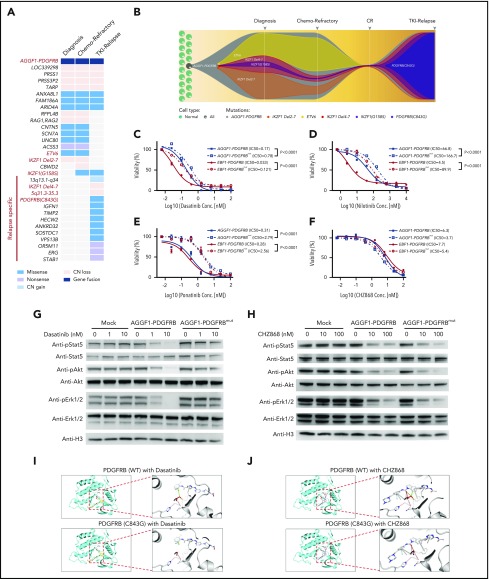
Figure 2.
Mutation of PDGFRBC843Gcaused TKI resistance in Ba/F3 cells with PDGFRB fusions. (A) Mutational landscape of leukemia cells at diagnosis, end of induction (chemotherapy refractory), and relapse. (B) A model of clonal evolution across disease progression. One subclone within the founding clone evolved to become the dominant clone at relapse, including mutations in PDGFRB. (C-F) Drug sensitivity of Ba/F3 cells with AGGF1-PDGFRB, EBF1-PDGFRB, AGGF1-PDGFRB carrying PDGFRBC843G (AGGF1-PDGFRBmut) or EBF1-PDGFRBmut upon dasatinib, nilotinib, ponatinib, and CHZ868 was detected by MTT assay. (G-H) Phosphorylation of Stat5, Akt, and Erk1/2 in Ba/F3 cells with AGGF1-PDGFRB, AGGF1-PDGFRBmut, and empty vector treated with dasatinib or CHZ868 as indicated concentration was detected by western blot. (I-J) The structure model of wild-type PDGFRB or mutant PDGFRBC843G with dasatinib or CHZ868. The cysteine (wild-type) or glycine (mutant) residue at position 843 is shown in red. All experiments were performed in triplicate. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001. CN, copy number; Conc., concentration; CR, complete remission IC50, 50% maximal inhibitory concentration.