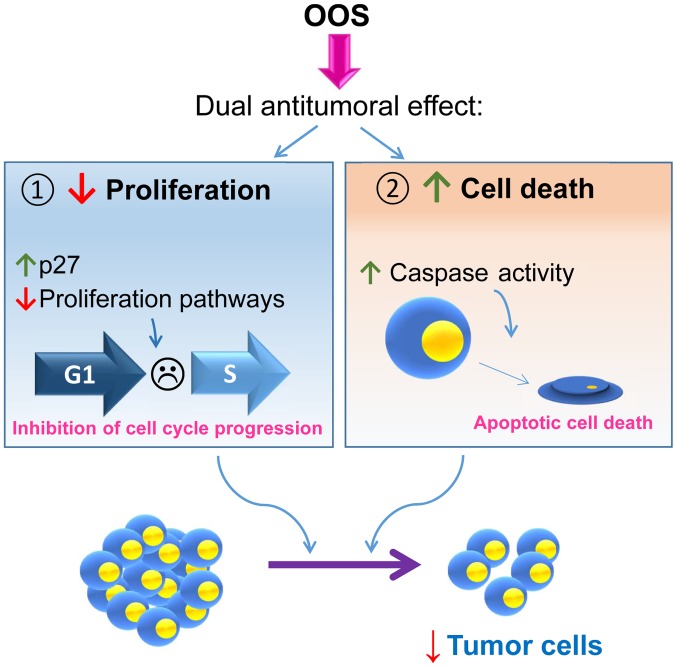
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism of action of OOS in SCLC. OOS exhibits a dual mechanism of action on SCLC both in vitro and in vivo. OOS induces, on the one hand, an inhibition of cell proliferation due to an increase in the cell cycle inhibitory protein p27 and the deceleration of the cell cycle. Moreover, an increase in caspase-dependent cell death is also stimulated upon OOS treatment. The combination of both actions provokes a decrease in tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. OOS, Ocoxin® oral solution; SCLC, small cell lung cancer.