Figure 1.
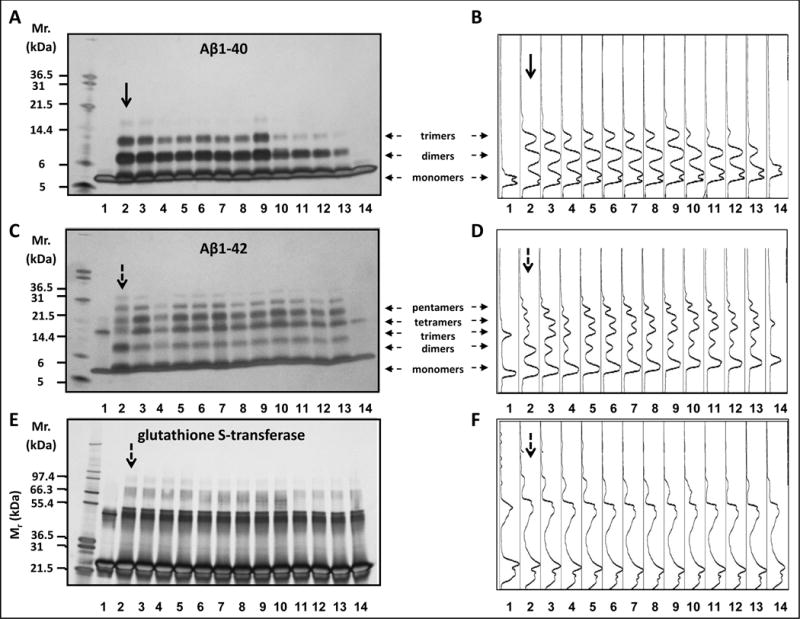
Select SCFAs potently interfere with protein-protein interactions among Aβ peptides. (a, c, e) Monomeric, dimeric and higher-ordered cross-linked multimeric Aβ1-40 (a), Aβ 1-42 (c) or GST (e) aggregates were visualized by silver staining of the gel. Shown are representative assays from three independent studies. (b, d, f) Densitometry intensity profiles for Aβ1-40 (b), Aβ1–21 (d) and GST (f). In (a-f, lane 1) Aβ1-40 (a,b), Aβ1-42 (c,d) or GST (e,f) alone without cross-linking. In (a-f, lanes 2–14) Aβ1-40 (a,b), Aβ1-42 (c,d) or GST (e,f) with cross-linking in the presence of vehicle (lane 2) or in the presence of individual SCFSs as follow: isobutyric acid at a SCFA:Aβ (or GST) molar ratio of 1:1 (lane 3) or 4:1 (lane 4), isovaleric acid at a SCFA:Aβ molar ratio of 1:1 (lane 5) or 4:1 (lane 6), acetic acid at a SCFA:Aβ (or GST) molar ratio of 1:1 (lane 7) or 4:1 (lane 8), propionic acid at a SCFA:Aβ (or GST) molar ratio of 1:1 (lane 9) or 4:1 (lane 10), butyric acid at a SCFA:Aβ (or GST) molar ratio of 1:1 (lane 11) or 4:1 (lane 12), valeric acid at a SCFA:Aβ (or GST) molar ratio of 1:1 (lane 13) or 4:1 (lane 14). In (a-d), horizontal arrows indicate monomers, dimers, trimers, tetramers and pentamers. In (a-f), vertical arrows indicate positive control studies in which Aβ1-40 (a-b), Aβ1-42 (c-d) or GST (e-f) were incubated in the absence of SCFA.
