Figure 2.
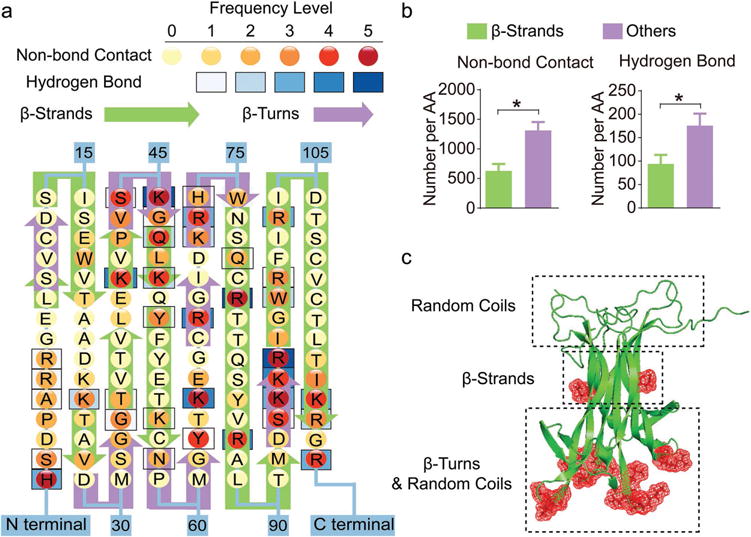
Binding sites with PEG-PLE primarily locate in regions that are rich in random coil and β-turn structures of BDNF. a) Frequency map of BDNF-polymer interactions on each amino acid of BDNF. The frequency levels of hydrogen bonds and nonbonding contacts are determined separately based on their total counts (summarized in Table S1, Supporting Information) in the trajectories obtained from four independent simulations with one BDNF dimer and one PEG-PLE chain. b) Quantification of BDNF–polymer interaction occurring on β-strands versus other structural domains. The result is presented as the number of occurrences averaged by the number of amino acids (denoted by AA in the figure) forming each structural domain. “*” denotes statistical significance between two groups (P < 0.05). c) Cartoon visualization of a BDNF dimer molecule with illustrations of predominant structural domains at each part of the protein. The red meshes represent amino acids that are actively involved in the binding between BDNF and its receptor, TrkB.
