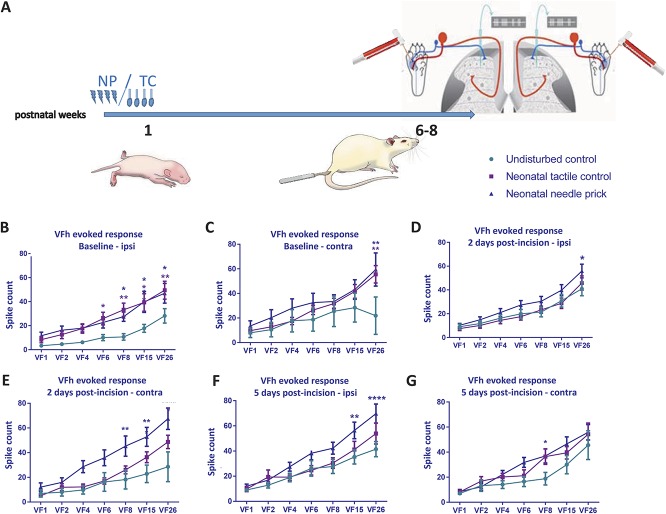
Figure 4.
Baseline and postinjury sensitivity to cutaneous punctate mechanical stimulation in adult dorsal horn neurons after neonatal repeated procedures. (A) Time course of the experiment. Responses in WDR neurons were recorded after graded von Frey hair (vFh) stimulation at baseline and postinjury in the ipsilateral (left panel) and contralateral (right panel) dorsal horn. Data were plotted as stimulus response curves (B) Baseline vFh sensitivity ipsilateral to injury was increased in NP animals and TC animals compared with UC. (C) Needle-prick animals displayed significantly increased vFh-evoked firing at 26 g in contralateral WDRs. (D) Two days after incision injury, ipsilateral stimulus response curves indicated slight hypersensitivity in NP compared with TC and UC at the highest vFh strength. (E) Two days after incision, NP animals were hypersensitive compared with TC and UC littermates in contralateral WDRs. (F) Five days after incision, NP animals were significantly more sensitive in ipsilateral WDRs than TC and UC. Changes were also observed in the contralateral dorsal horn. (G) Five days after incision, vFh-evoked contralateral neuronal firing was highest in the NP group. NP, needle prick; TC, tactile control stimulus; UC, undisturbed; vFh/VF, von Frey filament; WDR, wide-dynamic range. In all figures: data presented as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, between treatment comparisons. Asterisks are colour coded; dark blue asterisks represent between neonatal NP and undisturbed control comparisons; purple asterisks represent between neonatal tactile control and undisturbed control comparisons.