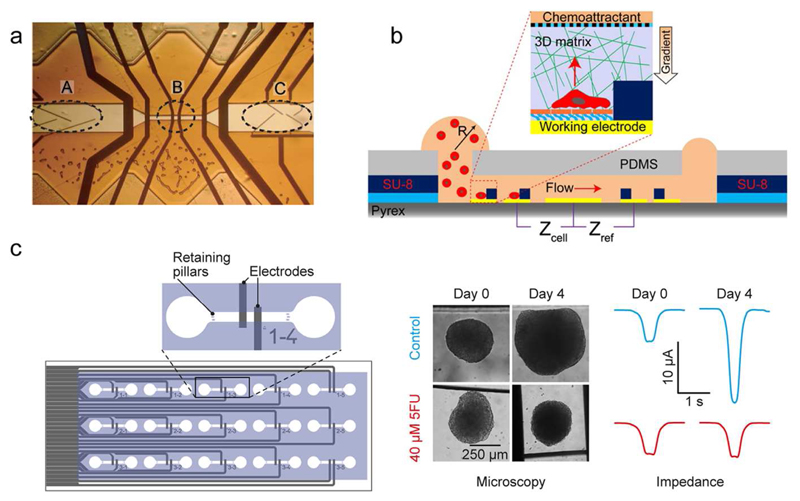
Figure 2.
EIS-based sensors. (a) An Iimpedance cytometer by featuring a flow-focusing region (A), measurement electrodes (B), and sorting electrodes (C). Adapted with permission from Cheung et al., Cytometry A 65, 124-132.20 Copyright 2005. (b) Integrated microfluidic device with an ECIS-sensor for studying single-cancer-cell migration in a 3D matrix. Adapted with permission from Nguyen et al., Anal. Chem. 85, 11068-11076.42 Copyright 2013. (c) Microfluidic chip with integrated parallelized EIS monitoring of the size of multiple cancer spheroids (adapted with permission from Bürgel et al., Anal. Chem 88, 10876-10883.51 Copyright 2016) Microtissues rolling over the electrodes generate a peak, whose amplitude is proportional to the size of the spheroids.