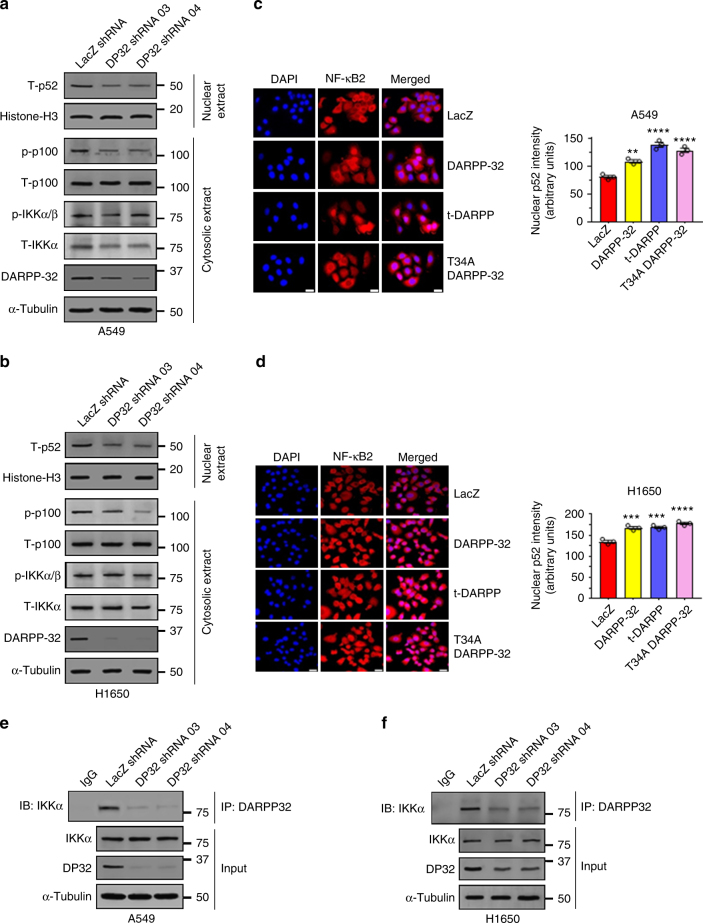
Fig. 4.
DARPP-32 knockdown inhibits non-canonical NF-ĸB2 signaling. a Nuclear fractions of A549 and b H1650 cells expressing control or DARPP-32 (DP32) shRNAs were immunoblotted with antibodies against total p52 (T-p52) and histone H3 (loading control). Cytosolic fractions were also collected and subjected to western blotting using antibodies against phosphorylated p100 (p-p100), total p100 (T-p100), phosphorylated IKKα/β (p-IKKα/β), total IKKα (T-IKKα), DARPP-32 and α-tubulin (loading control). c Immunofluorescence studies were performed using a monoclonal NF-ĸB2 antibody (that detects both p100 and p52 proteins) on A549 and d H1650 cell lysates expressing control or DARPP-32 shRNAs. Nuclei were labeled with DAPI. Average red fluorescence intensity of all nuclei was calculated using ImageJ software. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Each open circle on a graph represents an independent experiment. Scale bar, 20 µm. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test for multiple comparison. e A549 and f H1650 cells transduced with lentivirus encoding control or DARPP-32 shRNAs (DP32 shRNAs) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-DARPP-32 antibody and immunoblotted (IB) with antibody against IKKα. Total cell lysates (Input) were subjected to western blotting using antibodies against IKKα, DARPP-32 (DP32) and α-tubulin (loading control). All immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments. Uncropped images of depicted immunoblots are shown in Supplementary Figs. 18, 19