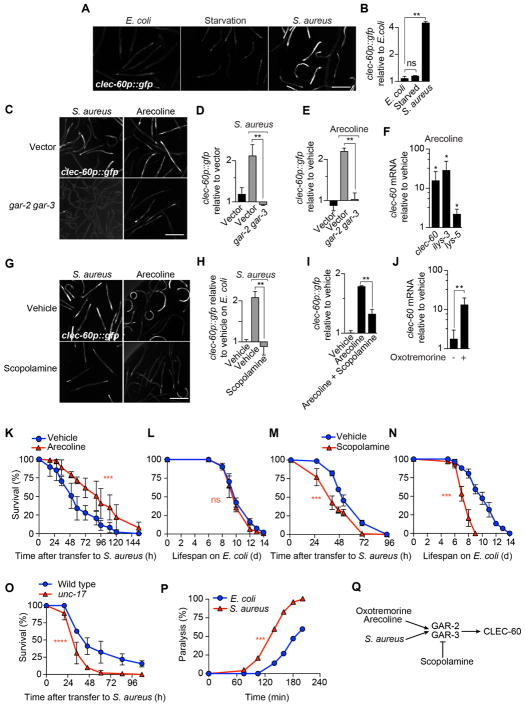
Figure 1. Muscarinic receptors control host defense against infection.
(A) Epifluorescence micrographs of animals expressing GFP from the clec-60 promoter (clec-60p::gfp) after 8 h of feeding on E. coli, starvation, or infection with S. aureus. (B) Quantitative analysis of (A). Data are mean ± SEM (two independent biological replicates, n ≥ 50 per condition). ** p ≤ 0.01 (see STAR★Methods for description of statistical methods). ns, not significant. (C) Representative epifluorescence micrographs of clec-60p::gfp animals that were reared on E. coli carrying empty vector (top row) or gar-2, gar-3 double RNAi (bottom row), and subsequently infected 16 h with S. aureus (left column) or treated for 16 h with 5 mM arecoline (right column). (D) Quantitative analysis of (C). Data are mean ± SEM (two independent biological replicates, n ≥ 50 per condition). (E) clec-60p::gfp expression after 16 h incubation of uninfected animals with 5 mM arecoline. Data are mean ± SEM (at least two independent biological replicates, n ≥ 50 per condition). (F) qRT-PCR of clec-60, ilys-3, and lys-5 in wild type animals incubated with 5 mM arecoline for 8 h, normalized to vehicle treated animals. Data are mean ± SEM (three independent biological replicates, n ≥ 3,000 per condition). * p ≤ 0.05. (G) Representative epifluorescence micrographs of clec-60p::gfp animals that were treated with vehicle (top row) or 5 mM scopolamine (bottom row), during 16 h infection with S. aureus (left column) or treated with 5 mM arecoline for 16 h (right column). (H) Quantitative analysis of infection in (G). (I) Quantitative analysis of scopolamine treatment in (G). Data are mean ± SEM (at least two independent biological replicates, n ≥ 50 per condition). (J) qRT-PCR of clec-60 in wild type animals treated with 1 mM oxotremorine for 8 h. Results are normalized to vehicle-treated animals. Data are mean ± SEM (three independent biological replicates, n ≥ 3,000 per condition). (K) Survival of wild type animals, treated with vehicle or 1 mM arecoline for 24 h prior to infection. Results are representative of 2 independent biological replicates. *** p ≤ 0.001. (L) Lifespan of wild type animals treated with vehicle or 1 mM arecoline for 24 h before transfer to E. coli OP50. Results are representative of 2 independent biological replicates. ns, p > 0.05. (M) Survival of wild type animals, treated with vehicle or 1 mM scopolamine during the entire course of infection. Results are representative of 2 independent biological replicates. (N) Lifespan of wild type animals on E. coli OP50, treated with vehicle or 1 mM scopolamine. Results are representative of 2 independent biological replicates. (O) Survival of wild type and unc-17 mutant animals infected with S. aureus. Results are representative of 2 independent biological replicates. (P) Aldicarb paralysis assays of infected and uninfected animals. Results are representative of at least 3 independent biological replicates. (Q) Schematic summary of results. Scale bars, 0.6 mm. Also see Figure S1.