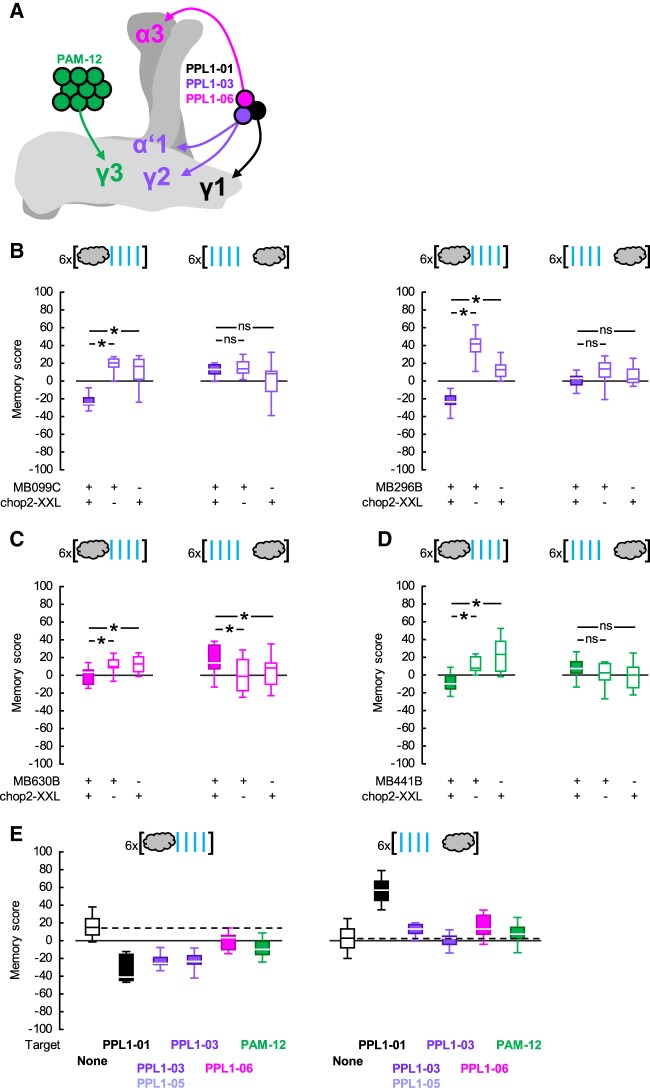
Figure 2.
Probing for timing-dependent valence reversal by PPL1-03, -06 or PAM-12 neurons. (A) The dopaminergic neuron types PPL1-01, -03, -06, and PAM-12 are sketched, respectively, in black, purple, pink, and green to show their cell body positions and the regions they innervate in the mushroom body (see also Table 1). The γ, α′/β′, and α/β lobes of the right mushroom body are sketched in light, darker, and yet darker gray, respectively. Please note that PPL1-01 neurons in addition innervate the mushroom body peduncle, not shown on the sketch. (B) (Left) The Split-Gal4 driver MB099C was used to express chop2-XXL in the PPL1-03 and -05 neurons. Upon repetitive odor → blue light training, MB099C;chop2-XXL flies had more negative memory scores compared to genetic controls, indicating learned avoidance (U-tests: MB099C;chop2-XXL versus MB099C: U = 0.00, P = 0.0009; MB099C;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 4.00; P = 0.0039; N = 8, each). In contrast, upon repetitive blue light → odor training, the scores of the MB099C;chop2-XXL flies did not differ from those of the controls (U-tests: MB099C;chop2-XXL versus MB099C: U = 30.00, P = 0.8748; MB099C;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 18.00; P = 0.1562; N = 8, each). (Right) The Split-Gal4 driver MB296B was used to express chop2-XXL in the PPL1-03 neurons. Repetitive odor → blue light training led to more negative scores in the MB296B;chop2-XXL flies than in the genetic controls, indicating learned avoidance (U-tests: MB296B;chop2-XXL versus MB296B: U = 0.00, P = 0.0009; MB296B;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 0.00; P = 0.0015; N = 8, 8, 7). In contrast, upon repetitive blue light → odor training, the scores of the MB296B;chop2-XXL flies were not different from those of the controls (U-tests: MB296B;chop2-XXL versus MB296B: U = 14.00, P = 0.0661; MB296B;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 27.00; P = 0.6365; N = 8, each). (C) The Split-Gal4 driver MB630B was used to express chop2-XXL in the PPL1-06 neurons. Repetitive odor → blue light training led to more negative scores in the MB630B;chop2-XXL flies than in the genetic controls, indicating learned avoidance (U-tests: MB630B;chop2-XXL versus MB630B: U = 38.00, P = 0.0193; MB630B;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 49.00, P = 0.0440; N = 14, 12, 13). Upon repetitive blue light → odor training, the MB630B;chop2-XXL flies had more positive scores than the genetic controls, indicating learned approach (U-tests: MB630B;chop2-XXL versus MB630B: U = 121.00, P = 0.0128; MB630B;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 135.00, P = 0.0203; N = 21, 22, 22). (D) The Split-Gal4 driver MB441B was used to express chop2-XXL in the PAM-12 neurons. Repetitive odor → blue light training led to more negative scores in the MB441B;chop2-XXL flies than in the controls, indicating learned avoidance (U-tests: MB441B;chop2-XXL versus MB441B: U = 18.00, P = 0.0021; MB441B;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 14.00; P = 0.0010; N = 13, 11, 11). Upon repetitive blue light → odor training, the MB441B;chop2-XXL scores tended to be more positive than those of the controls; this effect, however, did not reach significance (U-tests: MB441B;chop2-XXL versus MB441B: U = 141.00, P = 0.3700; MB441B;chop2-XXL versus chop2-XXL: U = 116.00; P = 0.0977; N = 19, 18, 18). (E) To provide an overview of the data in Figures 1D-left, 2B–D, the memory scores of all experimental genotypes are shown in comparison to a data set for genetic control scores pooled across experiments. Box plots, * and ns as in Figure 1.