Figure 5.
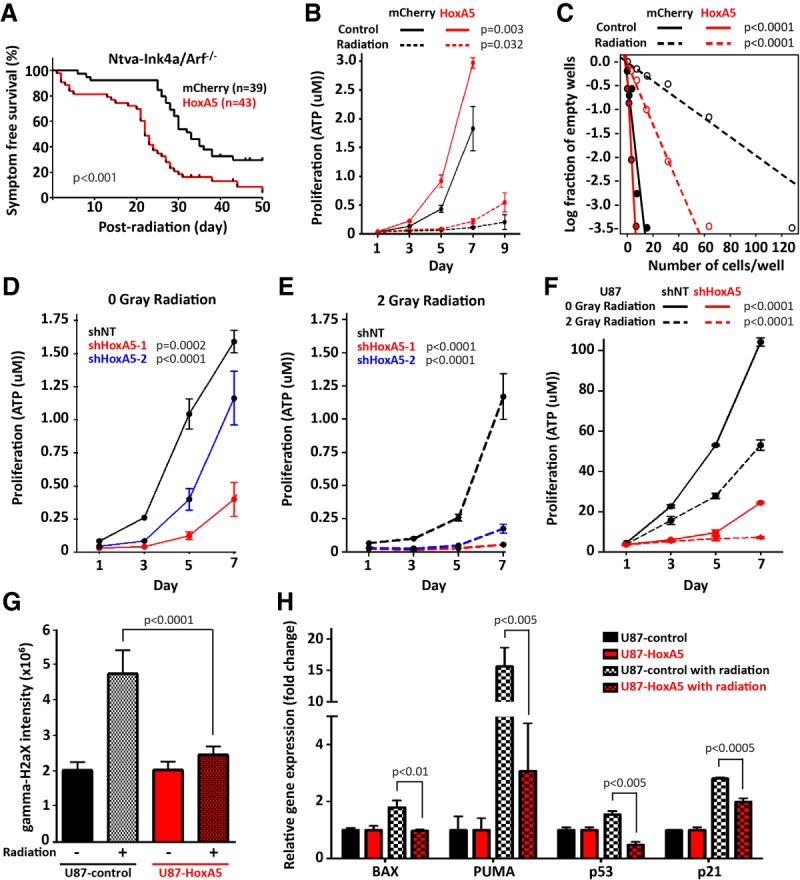
HoxA5 enhances radioresistance in glioblastoma cells. (A) Post-radiation survival is decreased for HoxA5-overexpressing glioblastomas in mice. (B) Proliferation in radiation-treated cultured mouse glioblastoma cells is increased with HoxA5 overexpression. (C) Limiting dilution clonal survival is increased with HoxA5 overexpression after radiation in glioblastoma cells. HoxA5 is associated with increased proliferation in vitro in mouse glioblastoma cells (D,E) and human U87 glioblastoma cells (F). (B–F) Cellular proliferation and clonality assays underwent statistical analysis for genotype effect by two-way ANOVA. (G) Radiation-induced DNA damage, as measured by γ-H2AX intensity, is inhibited by HOXA5 overexpression in human U87 glioblastoma cells. (H) HOXA5 mitigates radiation-induced up-regulation of cell cycle inhibitor- and apoptosis-related genes, including BAX, PUMA, p53, and p21 in human U87 glioblastoma cells. (G,H) Fluorescence intensity and gene expression assays underwent pairwise statistical analysis by the Mann-Whitney U-test.
