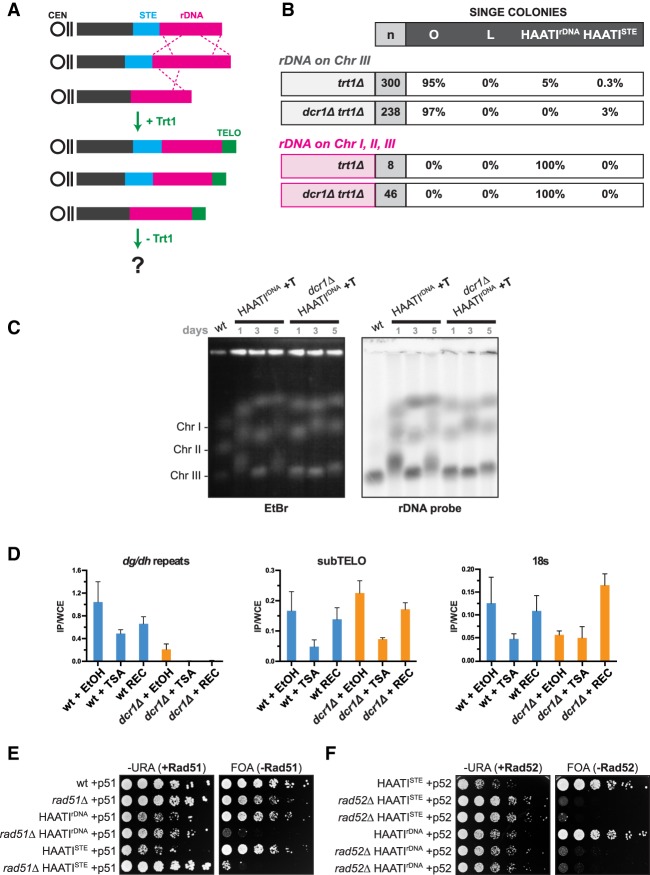
Figure 5.
RNAi-dependent pathways confer illegitimate rDNA translocation. (A) Schematic of HAATIrDNA+Trt1 cells forced into subsequent Trt1 loss. (B) Table summarizing the frequency of survivor formation under noncompetitive (single-colony) growth conditions. Single-colony data for “rDNA on chromosome III” (i.e., wild-type cells), taken from Figure 4D, are shown for comparison. (C) PFGE analysis of whole chromosomes hybridized with rDNA probe. Cultures of the indicated genotypes were propagated in liquid for 5 d. Aliquots were sampled at days 1, 3, and 5 for transformation with a plasmid encoding trt1+, which confers telomere addition and gel entry and thus a snapshot of chromosome length over time in the HAATIrDNA population. (D) Levels of H3K9me enrichment in wild-type and dcr1Δ (trt1+) cells before (+EtOH), during (+TSA [trichostatin A]), and after (+REC, for recovery) TSA treatment. Levels of the indicated genome regions in H3K9me2 immunoprecipitates were quantified by RT–PCR using primers for pericentromeric dg/dh repeats, subtelomeric (subTELO) regions, and the 18S rDNA. Means are shown; error bars represent standard deviations of three biological repeats. (E) Rad51 is essential for HAATI maintenance. Fivefold serial dilutions of the indicated strains on medium selecting for (FOA) or against (−URA) loss of plasmid expressing Rad51 (“+p51”). (F) Rad52 is essential for HAATI maintenance. Fivefold serial dilutions of the indicated strains on medium selecting for (FOA) or against (−URA) loss of plasmid expressing Rad52 (“+p52”).