Fig. 6.
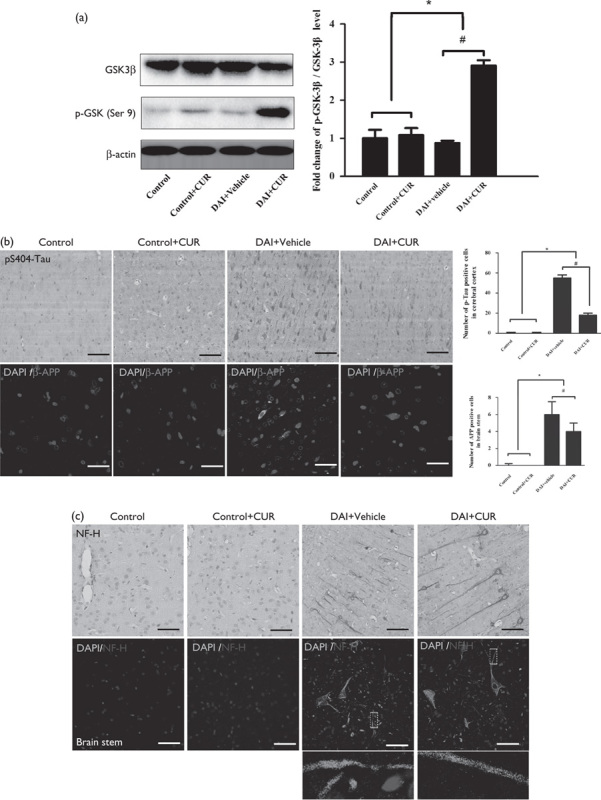
Curcumin reduced the accumulation of p-tau, β-APP, and NF-H after DAI. (a) The expression levels of GSK-3β and p-GSK-3β (Ser9) in cortical samples were detected by western blotting in each group. The expression of β-actin was used as an internal control. The bar graphs show the results for the ratio of p-GSK-3β (Ser9) to GSK-3β in each group. Values are presented as the mean±SD (n=4; *P<0.05, compared with the control group; #P<0.05, compared with the DAI+vehicle group). (b) Immunohistochemistry of p-tau (S404) and β-APP was performed to assess the aggregation of abnormal proteins in axons in each group. Scale bar=100 μm. The bar graphs show the numbers of p-tau-positive and β-APP-positive cells in each group. Values are presented as the mean±SD (n=4; *P<0.05 compared with the control group; #P<0.05 compared with the DAI+vehicle group). (c) Immunohistochemistry of NF-H was performed to assess axonal degeneration in the cerebral cortex and the brainstem in the each group. Scale bar=100 μm. CUR, curcumin; DAI, diffuse axonal injury.
