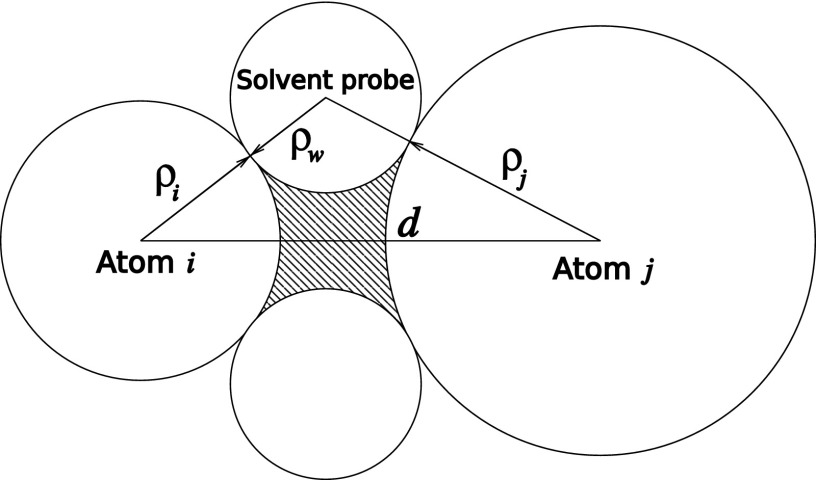
FIG. 2.
Sketch of the dielectric boundary (DB) around a pair of non-bonded solute atoms (ions) in a solvent, separated by a distance d. The DB is defined as a surface around the volume inaccessible to a solvent probe of radius [Richards-Connolly71,72 molecular surface (MS)]. This volume consists of two atomic spheres determined by atomic dielectric radii ρi and ρj and a region between these spheres (depicted as dashed area) inaccessible to the solvent probe and called the “Neck” region.