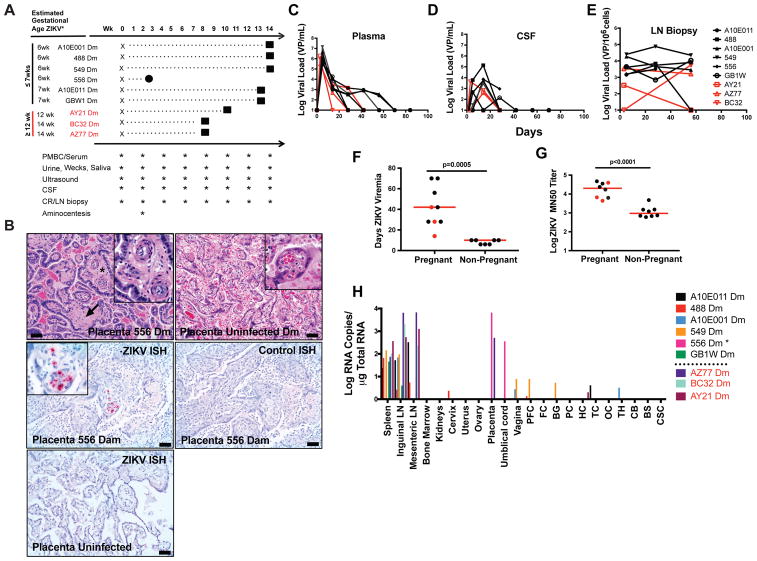
Figure 1. ZIKV infection in pregnant female rhesus monkeys.
A, Study schema and procedures. One fetal loss (556) occurred at week 3 post-infection (circle). All other fetuses were delivered by caesarian section at term (squares). B, Placental vasculitis (asterisks, inset) and villar sclerosis (arrow) in infected dam 549. C, Placenta from uninfected dam. D, In situ hybridization (ISH) for ZIKV RNA in placenta of dam 556 that aborted. E, ISH for control RNA in the same tissue section from 556 Dm. F, ISH for ZIKV RNA in placenta from uninfected dam. G, Longitudinal ZIKV viral loads by RT-PCR in maternal plasma. H, Longitudinal ZIKV viral loads by RT-PCR in CSF. I, Longitudinal ZIKV viral loads by RT-PCR in lymph node biopsies. J, Duration of ZIKV viremia in pregnant versus non-pregnant female rhesus monkeys (p=0.0005, unpaired t-test). K, Log ZIKV microneutralization titers (MN50) in pregnant versus non-pregnant female rhesus monkeys at week 8 post-infection (p<0.0001, unpaired t-test). L, ZIKV viral loads in tissues from infected dams by RT-PCR at term, except for 556 Dm which was at time of fetal loss. Scale bars = 50 microns. H&E hematoxylin and eosin, PFC prefrontal cortex, FC frontal cortex, BG basal ganglia, PC parietal cortex, HC hippocampus, TC temporal cortex, OC occipital cortex, TH thalamus, CB cerebellum, BS brain stem, CSC cervical spinal cord. Black names, lines, and dots reflect animals infected early in pregnancy at ≤7 weeks gestation. Red names, lines, and dots reflect animals infected later in pregnancy at ≥12 weeks gestation. Horizontal red bar reflects mean responses. See also Figure S1.