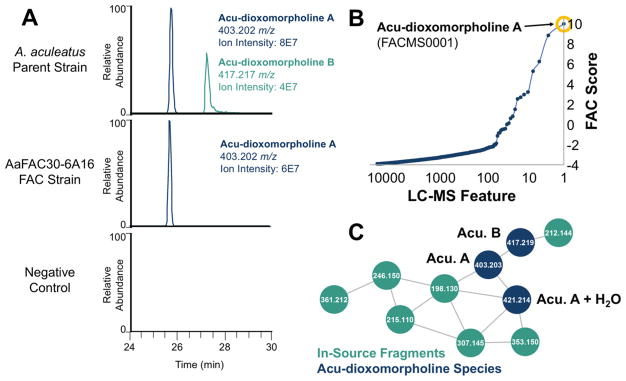
Figure 2.
FAC-MS data enabling the identification of the acu-dioxomorpholine biosynthetic gene cluster. (A) Both acu-dioxomorpholine A and B were detected in the A. aculeatus parent strain; however, only acu-dioxomorpholine A was detected in AaFAC30-6A16. Neither metabolites were detected in a negative control FAC (no insert). (B) A metabolite feature corresponding to acu-dioxomorpholine A was detected in the FAC strain AaFAC30-6A16. This feature was the highest scoring ion for this strain using a FAC Score which ranks features based on their uniqueness within the entire FAC library. (C) Mass spectral networking of A. aculeatus metabolomics data reveals structurally related features corresponding to the reported structure of acu-dioxomorpholine B, a desmethyl variant, acu-dioxomorpholine A, a hydrolyzed version of acu-dioxomorpholine A, and several fragment ions produced in the electrospray source of the mass spectrometer. Acu-dioxomorpholine A and B are abbreviated as Acu. A and Acu. B, respectively.