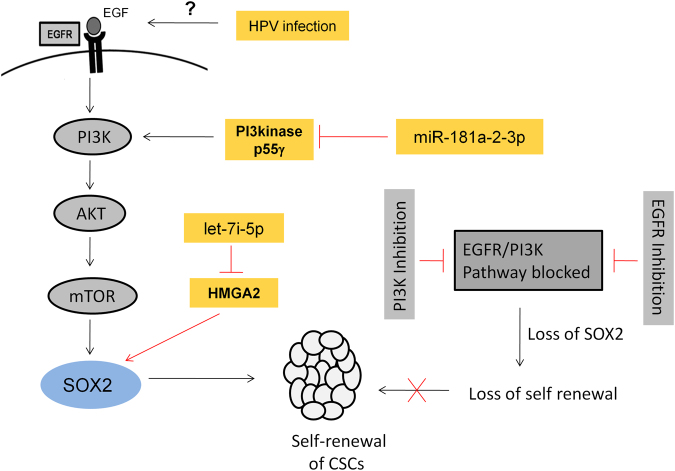
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram explaining the mechanism of CSC maintenance in cervical cancer via let-7i-5p, miR-181a-2-3p and EGF/PI3K/SOX2 axis. In this study, it was observed that exogenous EGF added to the media used for CSC enrichment induces the expression of PI3K and phosphorylates AKT, leading to the enhanced expression of SOX2. SOX2 silencing drastically reduced the CSC population in CaSki cells. The inhibition of EGFR phosphorylation and PI3K reduced the expression of SOX2 and subsequently suppressed the CSC population, thereby establishing the role of EGF pathway in the maintenance of cervical CSCs. While EGF pathway promotes CSC maintenance, let-7i-5p and miR-181a-2-3p counteracts by indirectly targeting SOX2 and thereby suppressing the cervical CSCs. let-7i-5p inhibits HMGA2 (an inducer of SOX2 expression) and miR-181a-2-3p inhibits PI3kinase p55γ (PI3K activator). Hence, activation of EGF pathway and inhibition of let-7i-5p and miR-181a-2-3p are vital for cervical CSC maintenance. The reported literature suggests that HPV infection may cause activation of EGF pathway. If proven, this would perhaps explain the formation of cervical CSCs and hence the origin of cervical cancer.