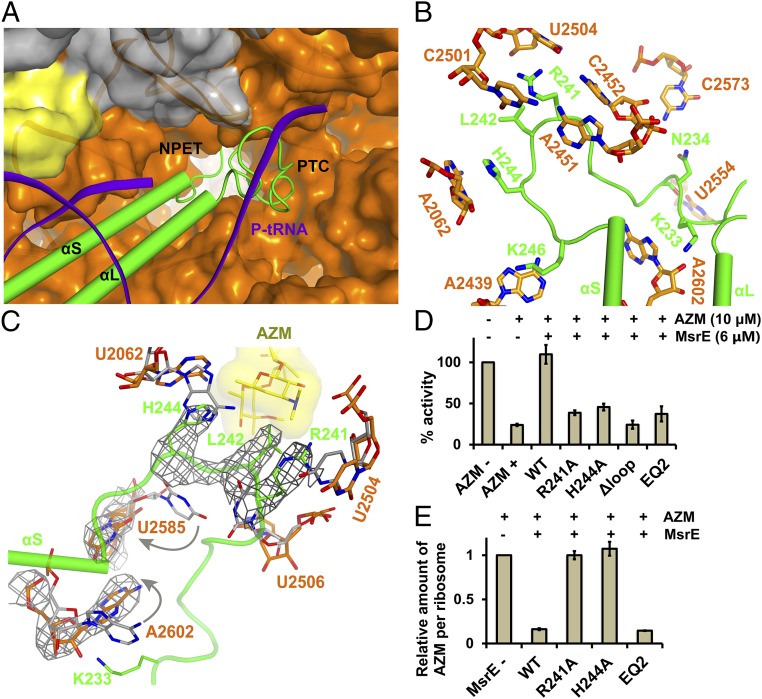
Fig. 5.
Structure and function of the MsrE domain linker extended loop. (A) The MsrE domain linker extended loop projects into the PTC/NPET region. The 50S subunit is shown in surface representation, and the P-tRNA acceptor stem is shown in cartoon representation. (B) Orientation of the MsrE extended loop and surrounding key PTC residues. (C) Conformational changes in the PTC and macrolide-binding site in the MsrE-ribosome complex compared with the post-peptidyl transfer state ribosome (gray) (30). Conformational changes are indicated by arrows. For reference, the AZM-binding mode is shown based on AZM-ribosome X-ray crystal structure (3). (D) Effect of WT and mutant MsrE proteins on E. coli-derived in vitro transcription/translation assay inhibited by AZM. Results are means of three independent repeats; error bars represent SDs. The uninhibited condition served as a standard. EQ2, MsrE(E104Q/E413Q) mutant. (E) Effect of MsrE on AZM displacement from ribosomes. Ribosomes treated with AZM were incubated with WT and mutant MsrE proteins preincubated with AMP-PNP and ATP, respectively. Ribosomes were pelleted through a sucrose cushion, and AZM was quantified using mass spectrometry. Results are means of three MS assays; error bars represent SDs. The no MsrE addition condition served as a standard.