Figure 5.
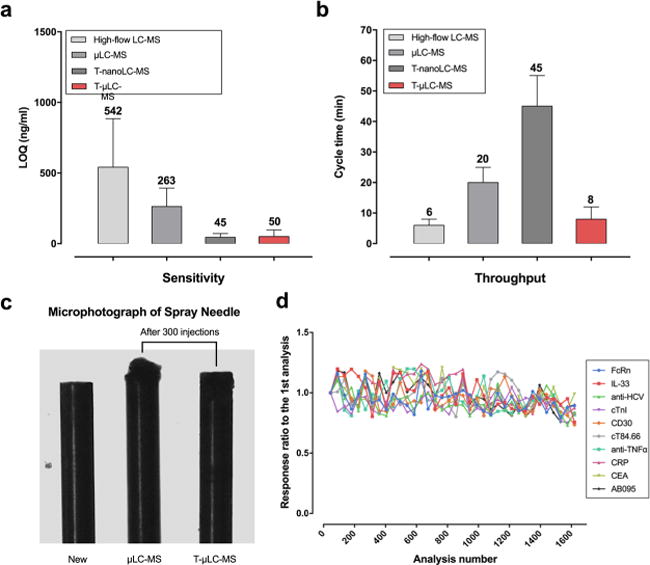
Evaluation of sensitivity, throughput, and robustness of the T-μLC-MS system. We compared T-μLC-MS with high-flow LC-MS (400 μL/min), μLC-MS (25 μL/min, without trapping), and trapping-nano-LC-MS (250 nL/min) by examining their (a) limits of quantification (LOQ) and (b) cycle times for the quantification of the 9 proteins (excluding cTnI) in nonenriched plasma or tissue samples. The same extent of separation of the target from the interfering peaks is achieved for each method (note: backgrounds are noisy for nonenriched samples). (c) Photomicrographs comparing new spray needles to these after 300 injections of plasma samples using μLC-MS (middle) and T-μLC-MS (right). (d) Graph demonstrating the high robustness of the T-μLC-MS system. Plasma samples spiked with the 10 SPs were injected every 60 injections of other plasma or tissue samples. No appreciable decreases in the signals were observed after >1600 injections.
