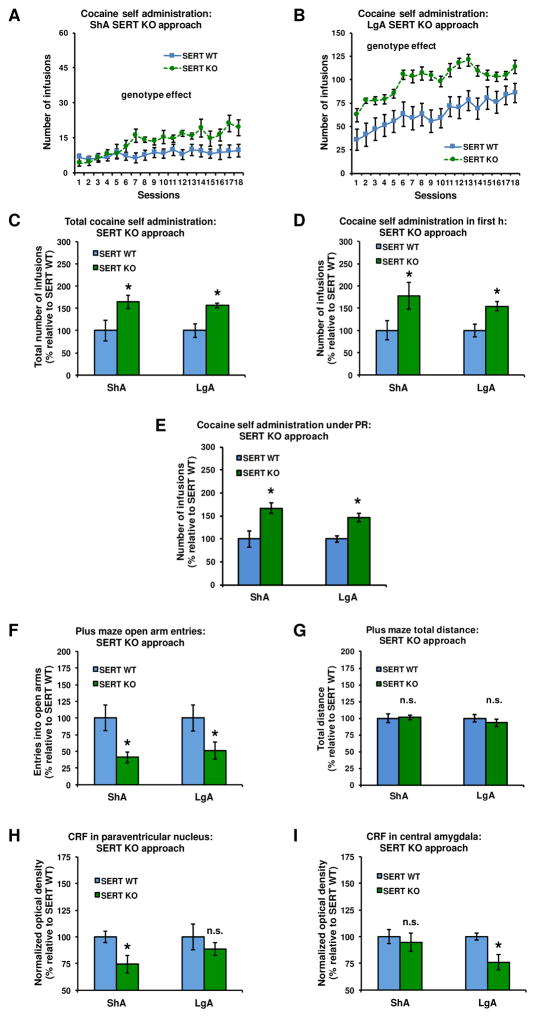
Figure 3.
Constitutive SERT KO increased daily cocaine intake (A–B), cumulative cocaine intake (C), intake during the first h of the final self-administration session (D), and intake during a PR schedule of reinforcement (E) in rats exposed to either ShA or LgA cocaine self-administration. SERT KO also reduced open arm entries, but not locomotor activity, on the EPM after both durations of cocaine access (F and G). The SERT KO-induced increase in ShA cocaine intake (A) was accompanied by a reduction of CRF immunodensity levels in the PVN (H), but not CeA (I). In contrast, the SERT KO-induced increase in LgA intake of cocaine (B) was accompanied by a reduction of CRF in the CeA (I), but not PVN (H) (see Supplementary Figure S8 for representative pictures). In panels C–I, data are normalized to values obtained in SERT WT counterparts (see Supplementary Table S5 for absolute values). *Significant change (P<0.05) vs SERT WT, n.s: no significant change. ShA: SERT WT (blue): n=14, SERT KO (green): n=12; LgA: SERT WT (blue): n=10, SERT KO (green): n=11.