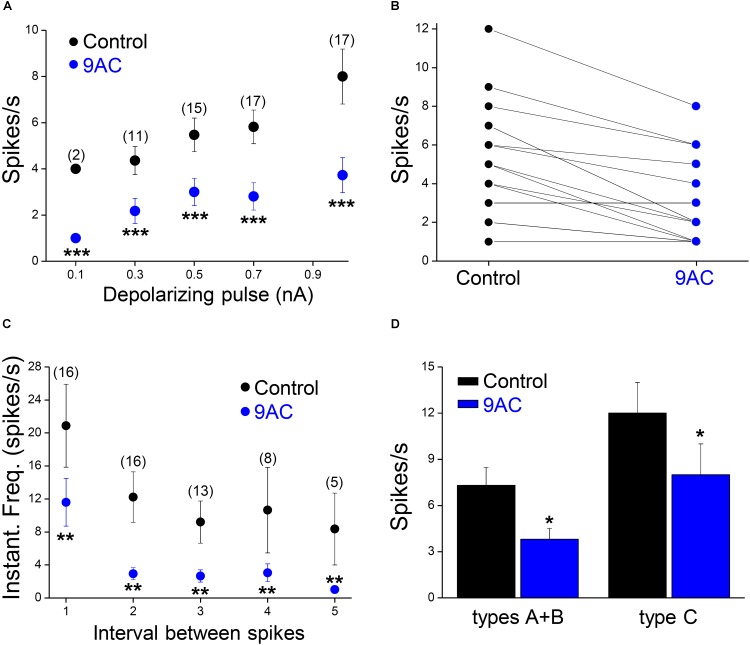
FIGURE 3.
The chloride channel blocker 9AC reduces firing frequency and instantaneous frequency in almost all sympathetic neurons. (A) The reduction in firing frequency was observed for all the amplitudes of the depolarizing pulse used (black circles for control solution and blue circles for 2 mM 9AC solution). Only cells firing two or more spikes in the control were considered (numbers in brackets). (B) The number of APs elicited is larger in control than in 9AC in the majority of cases (15 out of 18) with 0.5 nA depolarizing pulses. (C) The instantaneous frequency of spikes was reduced for all of the five first intervals between consecutive spikes studied with depolarizations of 1.0 nA. Symbols are the same as in A. The number of cells studied in each case is shown in brackets. (D) Effects of CaCC blockade with 9AC on firing frequency separately in cells with (types A and B) and without (type C) ADP for 1.0 nA depolarizing pulses. Paired t-test: ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (A,C) and Student’s t-test: ∗P < 0.05 (D).