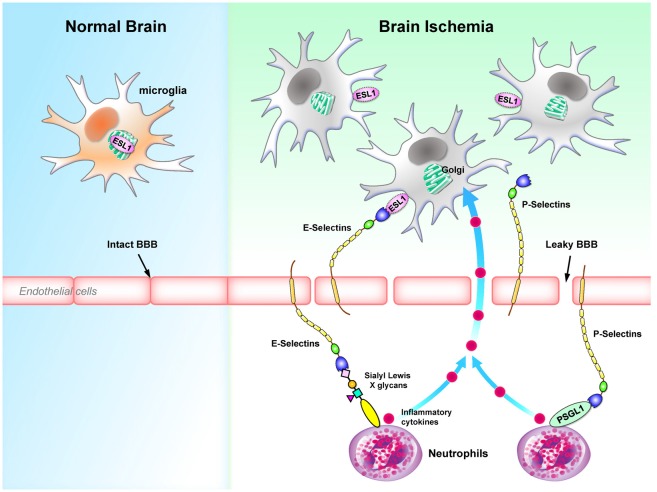
Figure 5.
Selectins regulates microglial activation and homing to sites of inflammation during brain ischemia. E-selectins and P-selectins that bind to Sialyl Lewis X glycans are up-regulated in endothelial cells during brain ischemia. Binding of selectins serves as a homing mechanism to retain Sialyl Lewis X glycans-containing cells close to endothelial cells. In particular, ESL1 located in the Golgi compartments of microglia is translocated to the plasma membrane and binds to E-selectins on the surface of endothelial cells (Werneburg et al., 2016). In contrast, P-selectins cause a transient leakage of BBB (Jin et al., 2010). P-selectins bind to PSGL1 on neutrophils, which secrete inflammatory cytokines and further activate microglia in the CNS (Schneider et al., 2015; Atangana et al., 2017). BBB, blood-brain barrier; ESL1, E-selectin ligand-1; PSGL1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1.