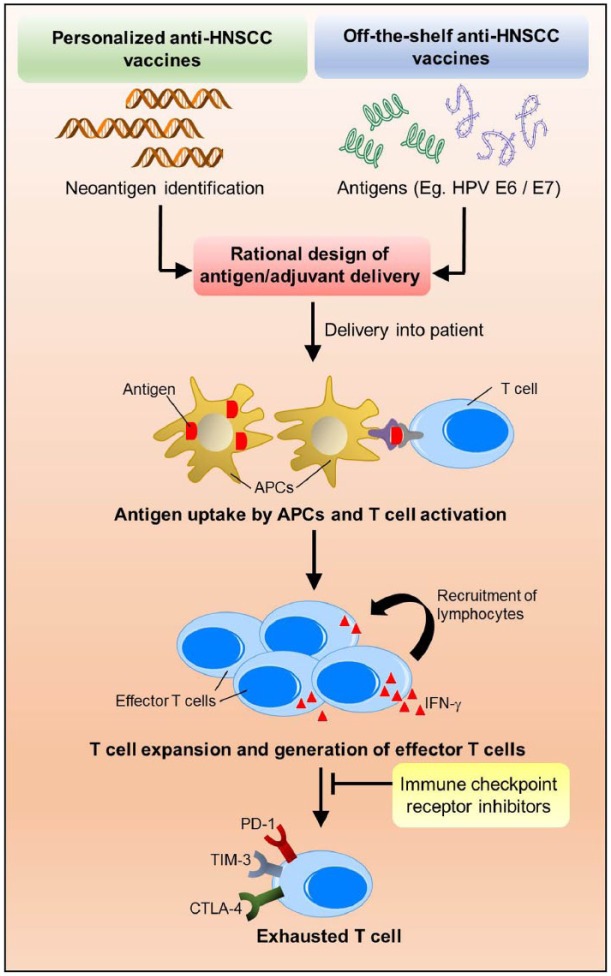
Figure 2.
A combination of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) vaccines with immune checkpoint receptor (ICR) inhibitors to promote durable and effective responses in patients with HNSCC. HNSCC vaccines may be personalized vaccines based on whole exome sequencing–dependent neoantigen identification or off-the-shelf vaccines based on unique antigens, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) E6/E7 oncoproteins. Next, rational designs to enhance the intracellular delivery are essential to reprogram antigen-presenting cell–mediated immune detection of cancer. Activated antigen-presenting cells will enhance vaccine-specific T-cell expansion and epitope spreading to build a more diverse effector T-cell repertoire. However, some of the newly generated effector T cells will inevitably become exhausted with significantly high expression levels of ICR. Hence, a rational combination with ICR-targeted therapies likely sustains the function of the effector T cells and improves durability of the response.