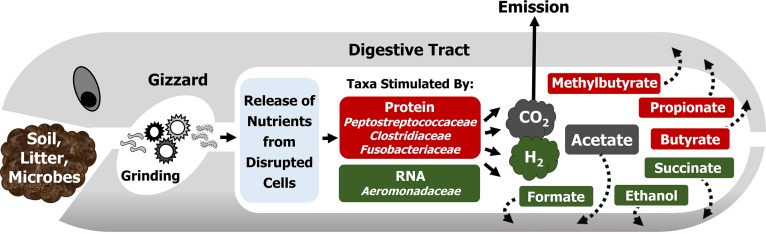
FIG 6.
Hypothetical model illustrating the potential trophic interactions between the earthworm L. terrestris and ingested soil microorganisms capable of fermenting protein- and RNA-derived organic carbon, a source of which can be gizzard-disrupted cells. Broken arrows symbolize the utilization of fermentation products by the earthworm.