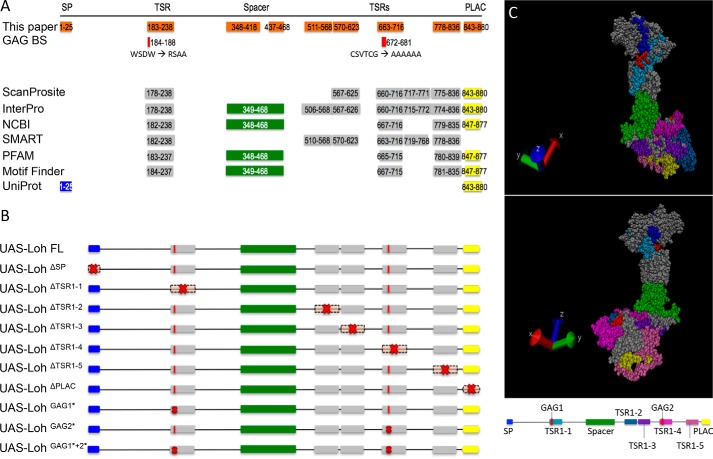
Figure 1.
Lonely heart domain structure and constructs used in this study. A, the Lonely heart isoform A sequence (GenBankTM entry AAF52956.3) was used to identify functional motifs. An N-terminal signal peptide, a variable number of thrombospondin repeats type I, an ADAM spacer region, and a single C-terminal PLAC domain were recognized by ScanProsite, Interpro, NCBI, SMART, PFAM, Motif Finder, and UniProt. Additionally, two putative glycosaminoglycan (GAG) binding sites were identified that locate within two thrombospondin repeat type I motifs (44, 45). Numbers depict the respective amino acid positions. B, Lonely heart constructs used in this study. Red crosses indicate mutated protein motifs. Nomenclature indicates deletions (Δ) or point mutations (*). Due to algorithm-dependent, inconsistent predictions of the TSR1 domains, constructs were generated based on the protein structure proposed previously (13). SP, signal peptide. C, 3D model of Lonely heart with color-coded protein domains. All thrombospondin domains locate to the surface of the protein. Modeling was performed using YASARA (42) and VMD version 1.9.3 (University of Illinois).