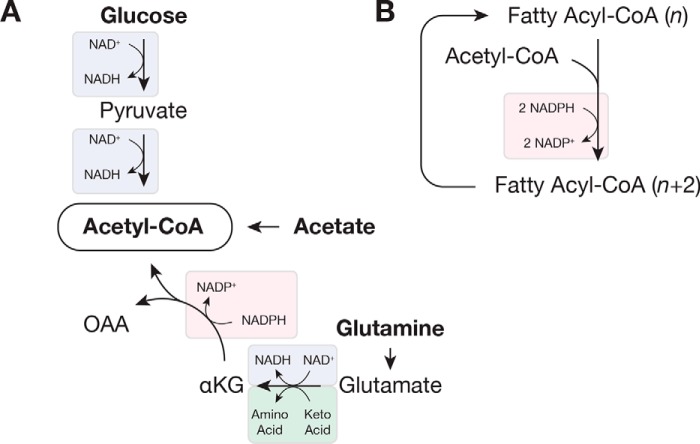
Figure 3.
Redox reactions involved in fatty acid synthesis. A, acetyl-CoA can be synthesized from glucose, glutamine, or free acetate, and each pathway relies on different redox cofactors. B, fatty acid synthesis and elongation use two molecules of NADPH per molecule of acetyl-CoA. In this figure, two carbon atoms from acetyl-CoA are added to a fatty acyl-CoA containing n carbon atoms. Substrate oxidation is indicated in blue; substrate reduction is in pink; and transamination is in green. Abbreviations used are: αKG, α-ketoglutarate; OAA, oxaloacetate.