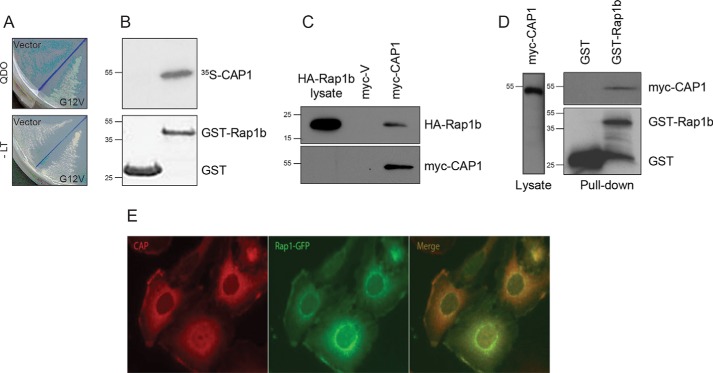
Figure 1.
Rap1b interacts with CAP1. A, two-hybrid isolation of a C-terminal fragment of human CAP1. The activation domain fusion plasmid expressing the C terminus of hCAP1 was cotransformed with empty vector pGBKT7 (Vector) or bait plasmid expressing G12V-Rap1b (G12V) and plated on selection medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and Ade (QDO; top) versus medium lacking only Trp and Leu (−LT; bottom). B, direct CAP1–Rap1b interaction. Immobilized GST or GST-Rap1b proteins (Coomassie Blue stain shown in lower panel) were incubated with [35S]methionine-labeled in vitro translated CAP1. After extensive washes, samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE. Once dried, radioactivity was visualized by fluorography using a phosphorimaging system (representative image of n = 2). C, in vivo Rap1b and CAP1 interaction. Empty vector (myc-V) or pCMV-myc-CAP1 was cotransfected with HA-Rap1b in HEK293T cells. After 48 h, cell lysates (normalized for equal HA-Rap1b signal) were immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc antibody (9E10), and the presence of Rap1b in the immunocomplex was assessed by Western blotting with an HA-specific antibody. D, in vivo Rap1b and CAP1 interaction. HEK293T cells were transfected with myc-CAP1 plasmid along with GST empty vector or GST-Rap1b mammalian expression plasmids. After 48 h, cell lysates (normalized for equal myc-CAP1 signal) were pulled down with GSH-Sepharose beads. The presence of CAP1 in the complex was assessed by Western blotting with a myc-specific antibody. A representative experiment (n = 3) is shown for C and D. E, colocalization of CAP1 and Rap1b. PCCL3 thyroid follicular cells stably expressing GFP-Rap1b were stained with anti-CAP1 antibodies, and fluorescence microscopy was used to assess intracellular colocalization of CAP1 (red) and Rap1b (green) (representative image; n = 3).