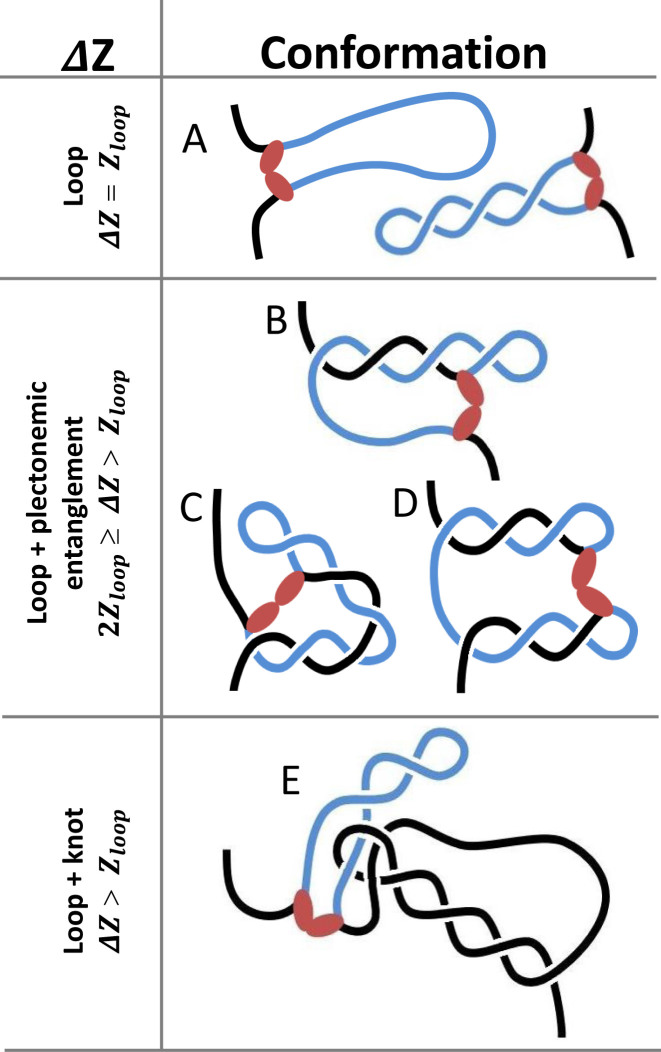
Figure 3.
Three distinct modes of entanglement trap different levels of supercoiling and topologically constrain different lengths of DNA. LacI might secure a loop without entangling any flanking DNA and shorten the tether by a value proportional to the loop size, Zloop (A). Alternatively, a blue looped segment may entangle with flanking black segments to further reduce the extension. For example, LacI may connect operators in a plectoneme and flanking DNA (B, C), in two different plectonemes (D), or in knotted DNA (E). Entanglements between the loop and flanking segments can reduce the extension by up to twice Zloop (B–D). Knotting between the loop and flanking segments can reduce the extension by more than Zloop (E).