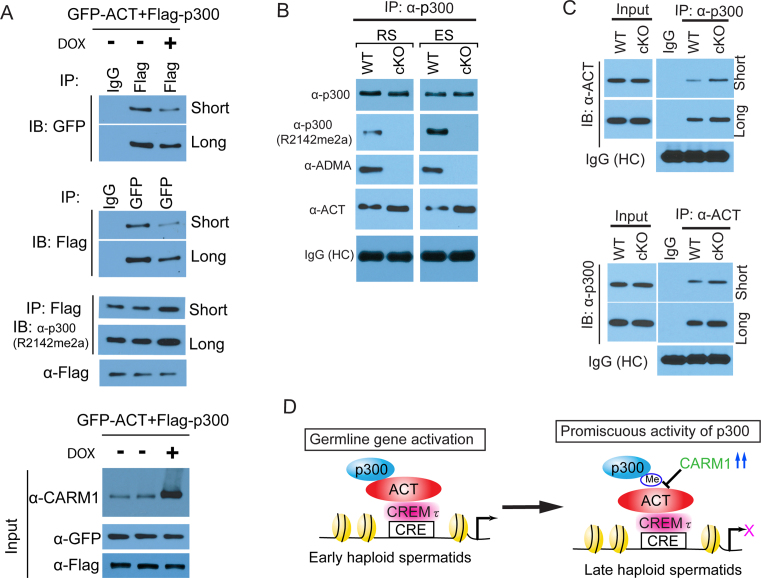
Figure 7.
p300 methylation at the GBD domain attenuated the interaction between ACT and p300 in vitro and in vivo. (A) The effect of overexpression of CARM1 on the interaction between ACT and p300. CARM1 was induced for overexpression by doxycycline in the inducible CARM1 Flip-in HEK293 cell line. Reciprocal co-IP was performed as indicated using Flag- and GFP-tag antibodies, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) p300 is endogenously methylated at R2142 in the haploid spermatids. Endogenous p300 protein was immuno-precipitated with specific p300 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with various antibodies as indicated. Note that Carm1 cKO abolished the ADMA mark on the p300 protein, and more bound ACT protein was detected upon Carm1 cKO in the p300 immunoprecipitates. The heavy chain (HC) of IgG served as an antibody loading control. (C) Endogenous co-IP was carried out in the round spermatids purified from the WT and cKO testes. Note that elevated binding affinity was observed between ACT and p300 in the cKO spermatids. (D) A working model for the role of Carm1-mediated methylation in haploid spermatids development. In the early stage of haploid spermatids, ACT recruits p300 co-activators to activate germline-specific target gene expression. In the late stage of haploid spermatids, a cohort of CREMτ/ACT-bound target genes must be temporally inhibited through the disassembly of the p300•ACT•CREMτ axis by the methylation of p300 by Carm1, for the last wave of metabolic reprogramming in the elongating spermatids.