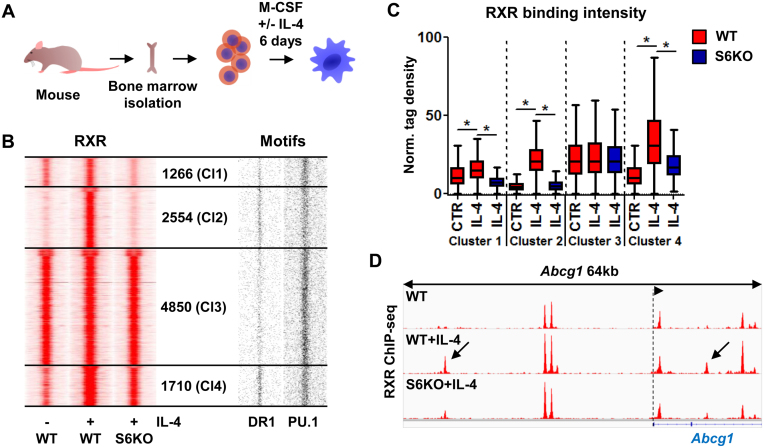
Figure 1.
Alternatively polarized macrophages greatly extend their RXR cistrome in an IL-4/STAT6-dependent manner. (A) Model system used to achieve alternative macrophage polarization. (B) Read distribution plots of RXR ChIP-seq signal intensities in wild type (WT) and Stat6 knockout (S6KO) macrophages either left untreated (–) or treated with IL-4 (+) (left). Clusters were discriminated based on IL-4 responsiveness and STAT6 dependence, and the number of genomic regions within them is indicated (middle). Distribution of DR1 and PU.1 motifs around RXR peaks (right). 1.5-kb regions are represented in 30-bp bins. (C) Box plot depicting the normalized tag density for each RXR clusters as shown on panel B. Significant differences are indicated with asterisks, determined by two-tailed paired t test, P< 0.0001. (D) Genome browser view about the RXR-bound genomic regions on the Abcg1 locus under the indicated conditions. Arrows indicate de novo RXR-bound regulatory regions, exhibiting STAT6 dependence.