Figure 1.
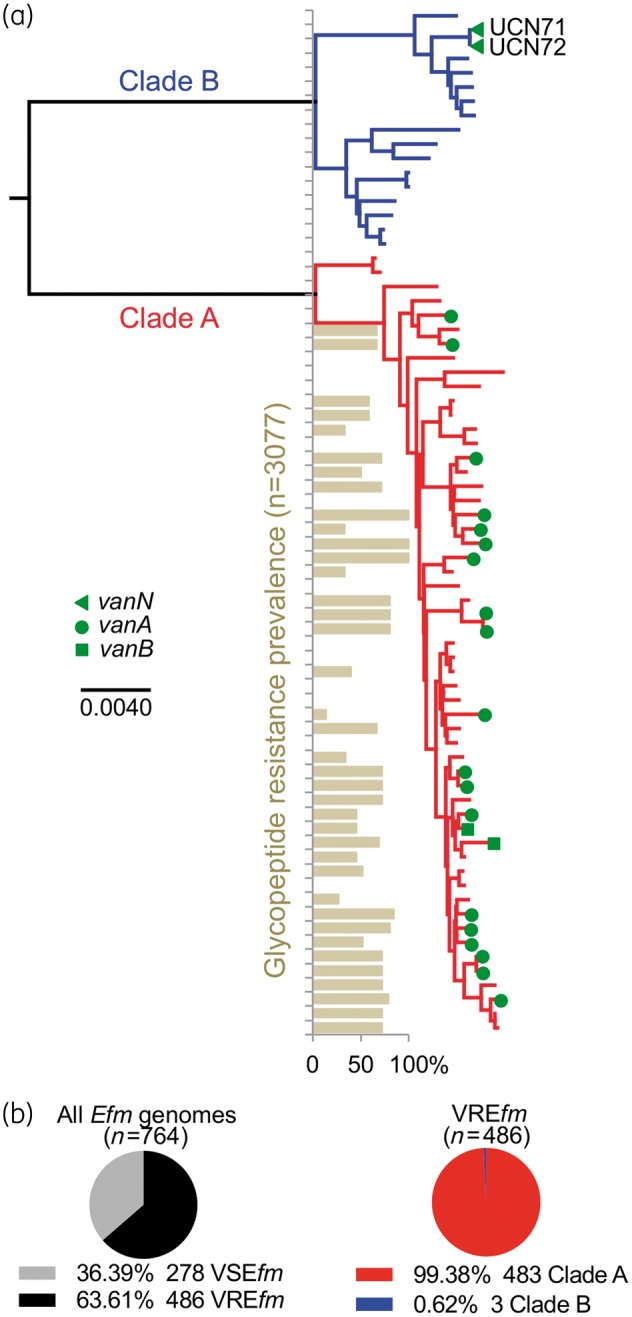
(a) VanN-type vancomycin resistance occurs in clade B E. faecium. Phylogenomic tree of a collection of E. faecium strains, including the VanN-type UCN71 and UCN72 isolates. The clade structure of the population is shown: clade B commensal strains (blue); and clade A hospital-adapted MDR strains (red). The vancomycin resistance genotype of each strain is shown. The prevalence of glycopeptide resistance of E. faecium strains from the MLST database for each particular ST is shown. Additional strain information is available in Table S1. (b) Prevalence of E. faecium strains (n = 764 publicly available genomes) harbouring (vancomycin-resistant E. faecium) or not (vancomycin-susceptible E. faecium) a vancomycin resistance cluster and distribution of vancomycin-resistant E. faecium within clades A and B. Efm, E. faecium; VREfm, vancomycin-resistant E. faecium; VSEfm, vancomycin-susceptible E. faecium.
