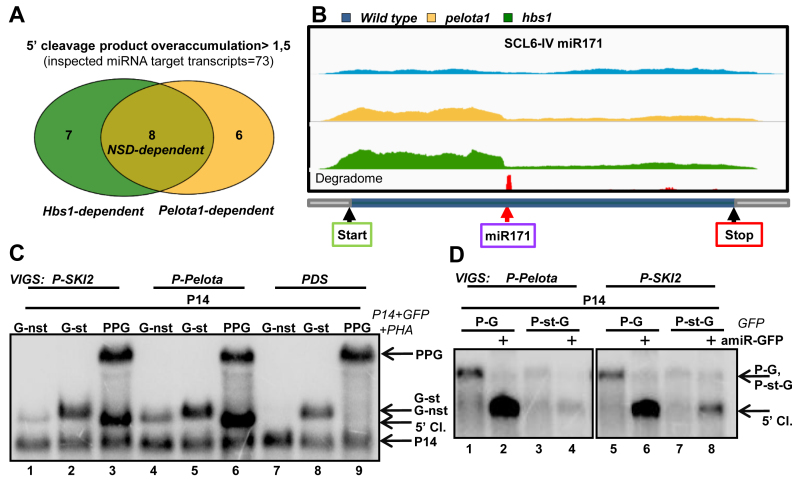
Figure 5.
SKI2 is required for the elimination of NSD target mRNAs. (A andB) NSD plays a role in the decay of 5′ cleavage fragments of miRISC in Arabidopsis. Comparative RNA-seq experiment was conducted from Pelota1 and Hbs1 T-DNA mutants (pelota1, hbs1) and from wild-type Arabidopsis plants. (A) Venn diagram shows the Pelota-, Hbs1- and the NSD-dependent Arabidopsis transcripts. The 5′/3′ coverage ratio of 73 miRNA target transcripts was analyzed. Pelota- or HBS1-dependent mRNAs are defined when the 5′ fragment overaccumulate >1.5-fold in the mutant relative to the wild type. If the 5′ fragment overaccumulate in both mutants, the mRNA was categorized as NSD-dependent. (B) The coverage of the SCL6-IV transcript. Yellow and green columns show the number of reads at a given position from pelota1 and hbs1 Arabidopsis mutants, while blue columns indicate the number of reads from wild type control. The degradome peak (red column) and the miRNA cleavage site (red arrow) are marked. (C) NSD reporter mRNAs accumulate to high levels in SKI2-deficient leaves. GFP-nst (G-nst) nonstop reporter construct was co-agroinfiltrated with P14 into the leaves of PDS-silenced (negative control), P-Pelota-silenced (positive control) and P-SKI2-silenced test plants. As controls, the same leaves were also co-agroinfiltrated with P14+G-st control and with P14+PPG vsiRISC sensor constructs. (D) SKI2 is involved in the decay of 5′ cleavage products of miRISC. Leaves of P-Pelota- and P-SKI2-silenced plants were agroinfiltrated in the presence or in the absence of amir-GFP with P14+PHA-GFP (P-G) fusion constructs, or with P14+P-st-G construct, in which a stop codon separates the PHA and the GFP reporter genes. The blot was hybridized with GFP 5′ fragment probe, stripped, and then reprobed for P14.