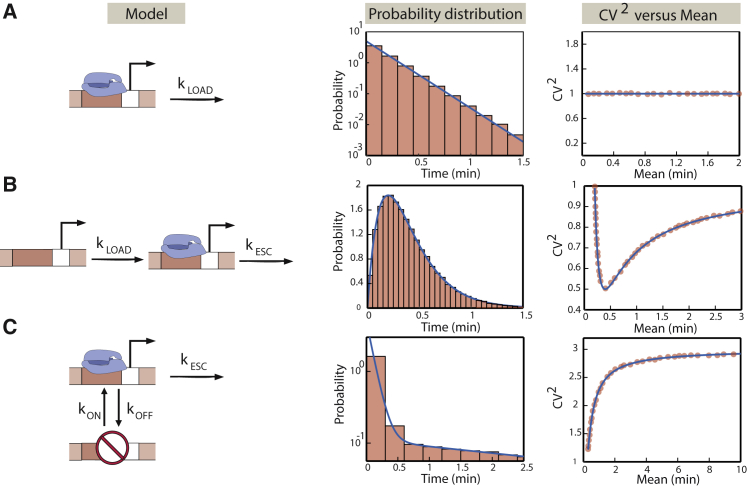
Figure 2.
Different models of transcriptional regulation lead to distinct signatures in the initiation times. (A) The one-step model of transcription initiation is depicted. Initiation happens at a constant rate kLOAD. The times between successive initiation events are exponentially distributed. The square of the coefficient of variation is plotted as a function of the mean, in which we change the mean by changing the rate of initiation, kLOAD. We confirm the analytical results using Gillespie simulations (65). The histograms and closed circles represent simulation results. (B) The two-step model of transcription initiation is depicted. Initiation happens in two sequential steps: the rate of RNAP loading onto the promoter occurs with rate kLOAD, followed by RNAP escaping the promoter, leading to transcript elongation at a rate kESC. The distribution of times between successive initiation events and the square of the coefficient of variation of the distribution as a function of the mean are shown. To change the mean, we change the rate of loading of RNAP polymerase molecules on the promoter, kLOAD. As in (A), simulation results are compared to the analytical results. (C) The ON-OFF model is depicted. The promoter switches between two states: an active and an inactive one. The rate of switching from the active state to the inactive state is kOFF and from the inactive to the active state is kON. From the active state, transcription initiation proceeds with a probability per unit time, kESC. The distribution of times between initiation events and the square of the coefficient of variation as a function of the mean are shown. Results from Gillespie simulations (65) are shown for comparison. To change the mean, we tune the rate kON of switching from the inactive to the active state. To illustrate the distinctive impact of the different initiation models on the distribution and moments of the times between successive initiation events, we use the following parameters: kOFF = 5/min, kON = 0.435/min, kLOAD= 0.14/min, and kESC= 0.14/min, which are characteristic of yeast promoters (36). To see this figure in color, go online.