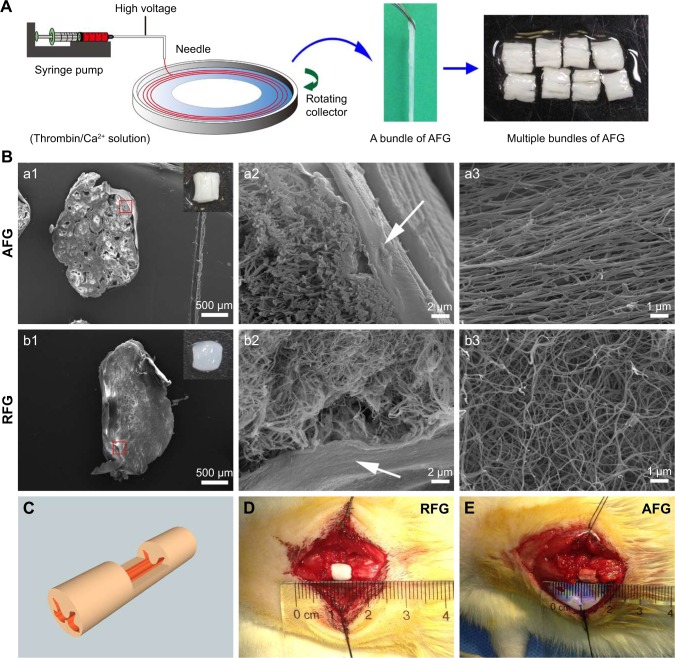
Figure 1.
Fibrin hydrogel scaffold and rat T9 dorsal hemisected SCI model. (A) The AFG fabrication process. (B) (a1–a2) and (b1–b2) SEM images of the cross sections of AFG and RFG scaffold reveal the hierarchically aligned structure of AFG and random fibrous structure of RFG, respectively; the insert pictures in (a1) and (b1) display gross images of the implanted AFG and RFG scaffolds; the arrows in (a2) and (b2) show the alginate film in the surface of the hydrogel for adhesive prevention. (a3 and b3) SEM images of the longitudinal sections of AFG and RFG scaffolds, demonstrating the aligned and random nanoscale fibrous structure, respectively. (C) Schematic illustration of the rat T9 dorsal hemisected model, and RFG and AFG scaffolds implantation (D and E).
Abbreviations: AFG, aligned fibrin hydrogel; RFG, random fibrin hydrogel; SCI, spinal cord injury; SEM, scanning electron microscope.