Fig. 5. Reciprocal roles for Foxp1 and Foxo1 in TH9 cell differentiation.
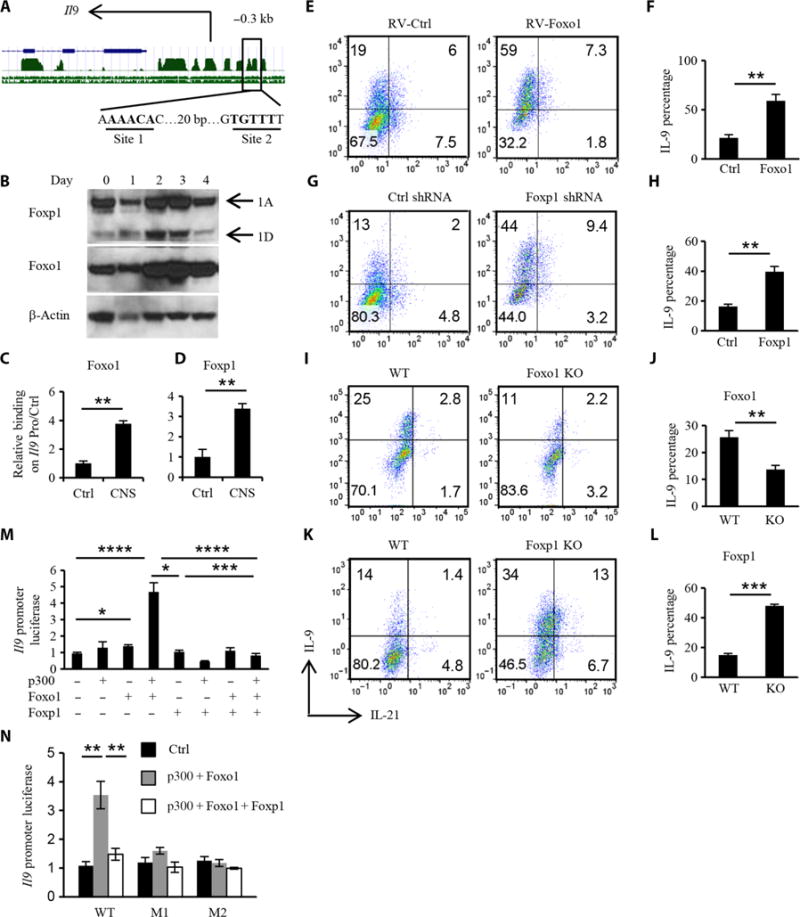
(A) Predicted Forkhead box transcription factor–binding sites on the Il9 promoter. Green peaks represent the conserved regions. The blue line represents the Il9 gene. Site 1 and site 2 are two predicted binding sites for Forkhead box transcription factors. bp, base pair. (B) Western blotting analysis of the abundances of Foxo1 and Foxp1 during TH9 cell differentiation over time. 1A, Foxp1A; 1D, Foxp1D. (C and D) ChIP analysis of the binding of Foxo1 and Foxp1 to the Il9 promoter in naïve OT-II CD4+ T cells. Data were normalized to the Il9 promoter control region. CNS, conserved noncoding sequence. (E and F) Naïve OT-II CD4+ T cells were cultured under the TH9 conditions for 24 hours, infected with control or mFoxo1 retrovirus (RV) in the presence of polybrene (10 μg/ml), and cultured for another 3 days under TH9 conditions. The cultured TH9 cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry to detect IL-9 and IL-21 in gated GFP+ (green fluorescent protein–positive) cells. (G and H) Preactivated CD4+ T cells were infected with control or Foxp1 shRNA (short hairpin RNA) lentivirus and differentiated for 4 days. Differentiated TH9 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to detect IL-9 and IL-21 in gated GFP+ cells. (I and J) Naïve CD4+ T cells were isolated from tamoxifen-treated wild-type (WT) and FoxoF/F ERT2Cre mice and cultured under TH9 conditions. Total differentiated TH9 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to detect IL-9 and IL-21. KO, knockout. (K and L) Effect of Foxp1 deficiency on TH9 cell differentiation. WT and Foxp1F/F ERT2Cre mice were treated with tamoxifen, and then isolated naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured under TH9 cell–differentiating conditions before total cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to detect IL-9 and IL-21. (M) Luciferase activity of the Il9 promoter combined with indicated factors to show the synergistic effect of Foxo1 and p300 and the inhibitory effect of Foxp1 on Foxo1-induced Il9 transcription. (N) Mutant Il9 promoters for site 1 (from AAACA to GAGTC, M1) and site 2 (from TGTTT to CCGGC, M2) were synthesized as indicated, and luciferase activity was analyzed to verify the specific binding locus of Foxo1 and Foxp1. Black column, control plasmids; gray column, p300 and Foxo1 plasmids; white column, p300, Foxo1, and Foxp1 plasmids. Data in (B) to (N) are from three independent experiments and are means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
