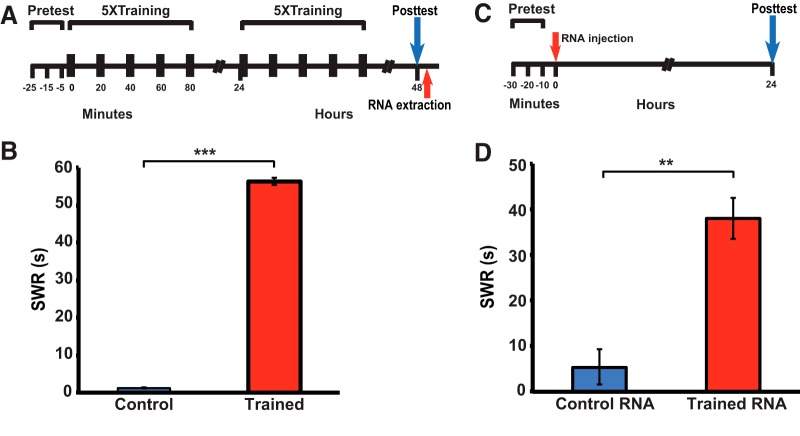
Figure 1.
RNA extracted from sensitization-trained donor animals induces long-term enhancement of the SWR in recipient Aplysia. A, Experimental protocol for inducing LTS in the donor animals. B, Mean posttest duration of the SWR in the untrained control (1.2 ± 0.1 s, n = 31) and trained (56.4 ± 2.0 s, n = 34) groups. The trained group exhibited significant sensitization, as indicated by the comparison with control group (Mann–Whitney test, U = 496, p < 0.001). C, Experimental protocol for the RNA injection experiments. The first pretest occurred 2–3 h after the posttest for the behavioral training (A). D, Mean duration of the SWR measured at ∼24 h after the injection of RNA for the control RNA (5.4 ± 3.9 s, n = 7) and trained RNA (38.0 ± 4.6 s, n = 7) groups. The two groups differed significantly (U = 30, p < 0.003). Furthermore, Wilcoxon tests indicated that the difference between the pretest and posttest for the trained RNA group was significant (W = 28, p < 0.02), whereas it was not significant for the control RNA group (p > 0.2). The bar graphs in this and the following figures display means ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s., nonsignificant.