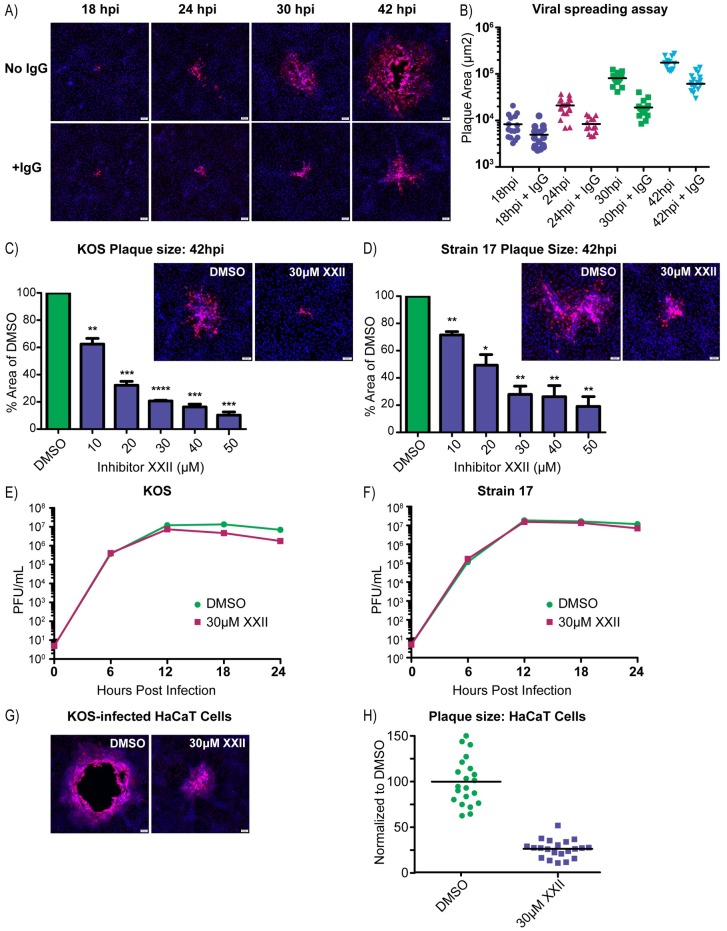
Fig 6. PTP1B inhibitor XXII blocks cell-to-cell spread.
(A) Vero cells were infected with the KOS strain (100 PFU/well in 6-well plates) and incubated in infection medium or medium containing 5 mg/ml of pooled human IgG to neutralize extracellular virions. At 18, 24, 30, and 42 hpi, the cells were immunostained for the major capsid protein, VP5, and nuclei were stained with DAPI. (B) To quantify virus spreading, the areas of 10–15 VP5-positive plaques were measured per sample and these were plotted. (C and D) Vero cells were infected (100 PFU/well) with strains (C) KOS or (D) 17 and then treated with increasing amounts of inhibitor XXII, all in the presence of 5 mg/ml of pooled IgG. At 42 hpi, the cells were immunostained for VP5, and representative plaques are shown. The areas of 10–15 plaques were measured for each drug concentration and compared to those from the DMSO control. Data from three independent experiments were combined and are represented as the mean ±SD. A student T-test was used to determine statistical significance for samples compared to the DMSO control. (E and F) Virus replication assays were performed in Vero cells infected (MOI = 5) with strains (E) KOS or (F) 17. The cells were incubated in medium containing DMSO or 30 μM inhibitor XXII, and at 6-hour time points, duplicate samples were collected to measure the virus titers (cell lysate + medium), which were averaged and plotted. (G) Representative images of plaques produced by the KOS strain on HaCaT cells treated with DMSO or 30 μM inhibitor XXII in the presence of 5 mg/ml pooled IgG. (H) At 42 hpi, 20 plaques from each sample in (6G) were measured, and their areas were plotted relative to the average obtained for the DMSO control.