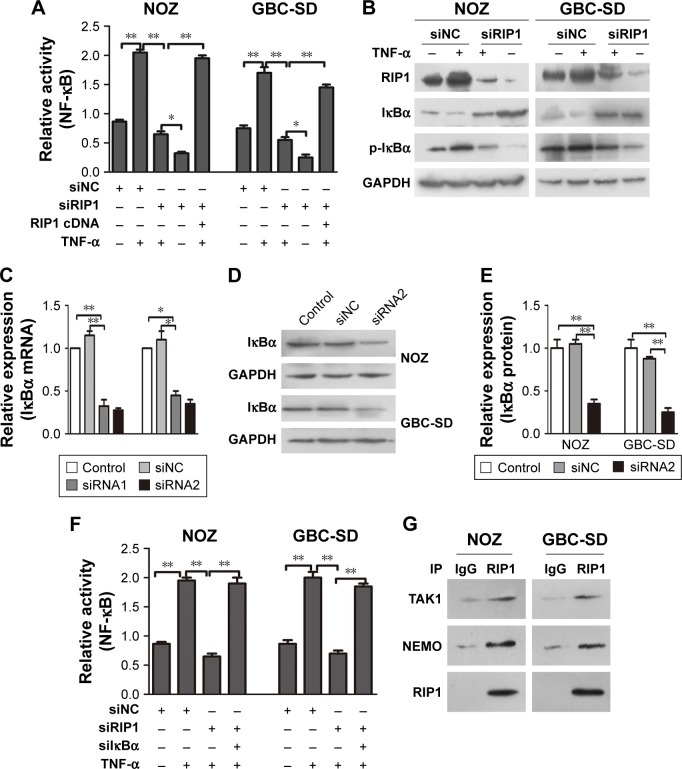
Figure 3.
RIP1 is essential for TNF-α-mediated NF-κB activation.
Notes: (A) NF-κB-luciferase activity was examined in the siNC and siRIP1 cell groups after being stimulated with 50 ng/ml of recombinant human TNF-α or left unstimulated for 24 h. Transfection of PcDNA3.1-RIP1 vector into the siRIP1 cell groups reversed the impairment of TNF-α-mediated NF-κB activation. (B) Western blot analyses of RIP1, iκBα, and p-iκBα expression in protein extracts from the siNC and siRIP cell groups that were stimulated with 50 ng/mL of recombinant human TNF-α or left unstimulated for 24 h. (C–E) Transfection of silκBα into NOZ or GBC-SD cells effectively inhibited iκBα mRNA and protein expression. (F) NF-κB-luciferase activity assays showed that knockdown of lκBα could reverse the impairment of TNF-α-mediated NF-κB activation in the siRIP1 cell groups. (G) immunoprecipitation analysis showed that TAK1 and NEMO are associated with RIP1. B, C, D and F; n=3, mean±SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Abbreviations: TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; GBC, gallbladder carcinoma; IκBα, inhibitor of NF-κB alpha; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator.