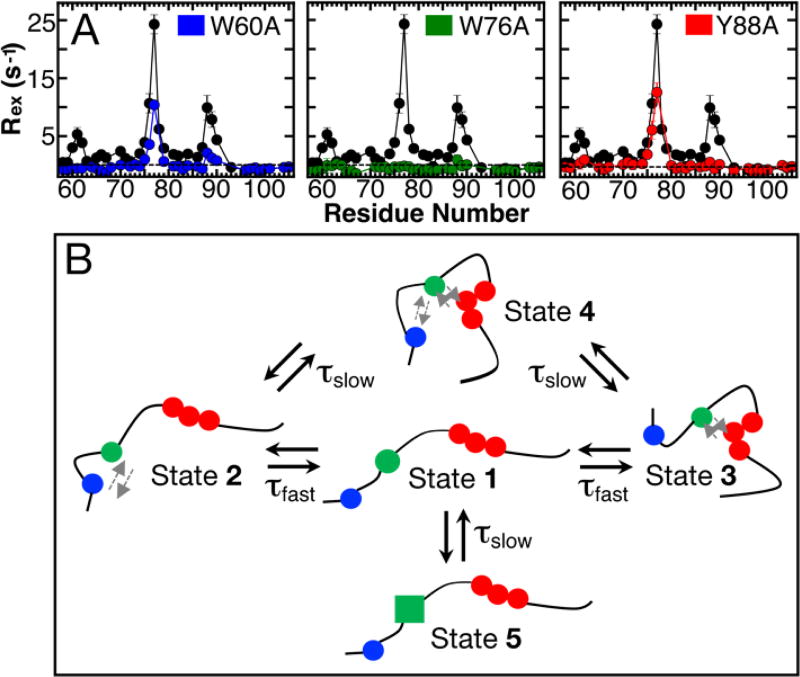
Figure 2. Mutagenesis of p27-D2 affect RD.
(A) Contributions of Rex for different point mutants of p27-D2 in which critical aromatic residues were substituted with alanine. Mutational analysis showed that W76 (green) abrogates all microsecond exchange in p27-D2 whereas the other mutants, W60A (blue) and Y88A (red), exhibit little exchange near the site of mutation and reduced exchange at the two non-mutated sites. Points in black correspond to wild-type p27-D2 data and the dashed black line is drawn at zero which indicates no detected exchange. Analysis of residual RD within the p27-D2 mutants can be found in Figure S8 and Table S4. (B) Schematic of the proposed model for observed microsecond p27-D2 dynamics. The three critical hydrophobic residues are colored in blue, green, and red and correspond to W60, W76 in the central region W76, and F87-Y89, respectively. The grey arrows indicate transient hydrophobic interactions.