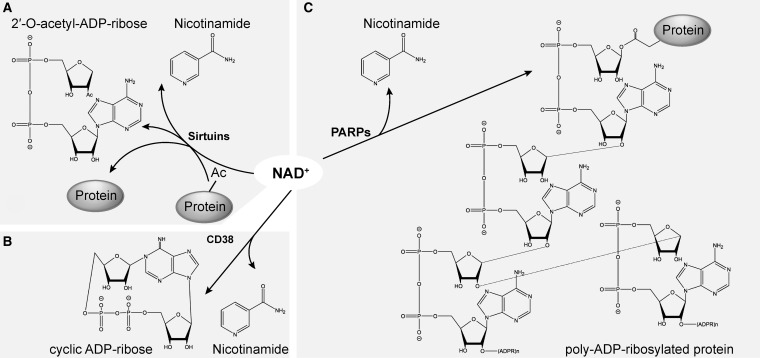
FIG. 2.
NAD+-consuming reactions. (A) NAD+ hydrolysis is coupled to deacetylation reactions by sirtuins. (B) Cyclic ADP-ribose production by ADP-ribosyl cyclases, including CD38 and CD157. (C) PARPs catalyze the addition of ADP-ribose to an acceptor protein following with extension and branching of the chain to form poly(ADP-ribose) polymers. Member of this family may also have mono-ADP-ribosylation activity, catalyzing the transfer of a single ADP-ribose moiety to the acceptor protein. All three reactions produce nicotinamide as a by-product. PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.