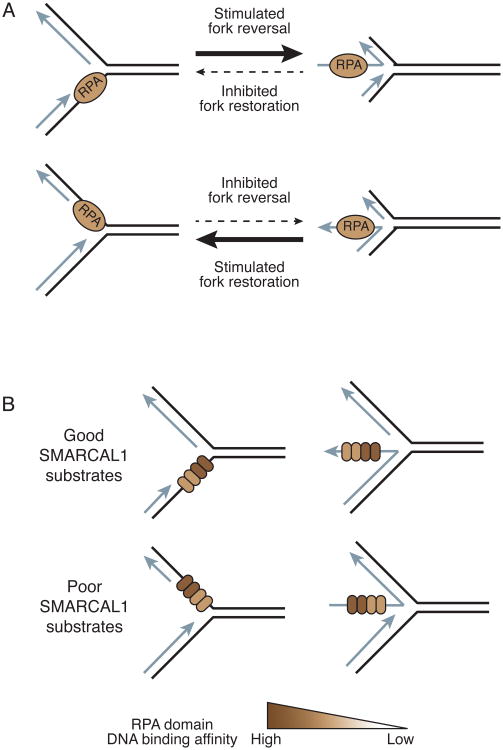
Figure 6.
The orientation of RPA binding to the replication fork substrate differentially regulates SMARCAL1. (A) Fork reversal is stimulated when RPA is bound to the leading strand template and is inhibited when it is bound to the lagging strand template. Fork restoration is activated when RPA is bound to a longer nascent leading strand and inhibited when it is bound to the nascent lagging strand. (B) RPA binds asymmetrically to ssDNA using four DNA binding domains with varying affinities. RPA stimulates SMARCAL1 when the two highest affinity DNA binding domains are located next to the fork junction and inhibits SMARCAL1 when the low affinity binding domains are located next to the junction.