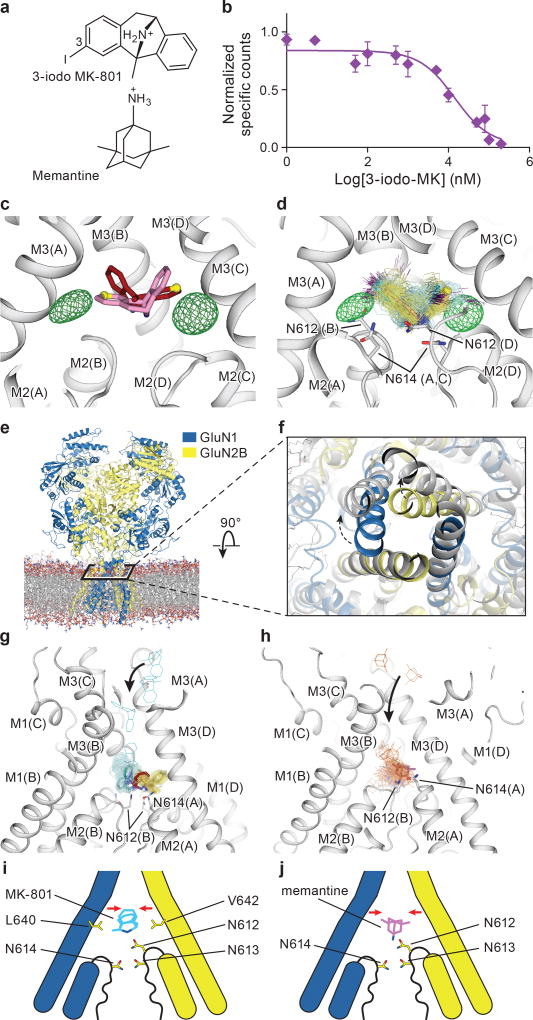
Figure 4. Mechanism of MK-801 and memantine binding.
a, The chemical structures of 3-iodo MK-801 and memantine. b, Plots of competition binding of cold 3-iodo MK-801 to the 3H-MK-801 bound ∆2 G610 receptor. The plot shows data from a representative experiment with error bars representing s.e.m. from triplicate measurements. c, The iodine anomalous density (green mesh) shown together with the positions of the MK-801 molecule in the crystal structure (red sticks) and the pseudo-2-fold related binding pose (salmon sticks). The carbon atoms at the 3 position are shown in yellow spheres. d, Positions of 3-iodo MK-801 obtained from MD simulations (Sim. 1) initiated from 3-iodo MK-801 docked in the binding pocket of the ∆2 structure. The movement of the iodine atoms (purple) of 3-iodo MK-801 clustered into two populations, in agreement with the anomalous difference densities (green mesh). In each of its two predominant poses (cyan and yellow sticks), MK-801 forms hydrogen bonds with N614 (GluN1) and N612 (GluN2B) (gray sticks). e, Simulation snapshot of ∆2 NMDA receptor (GluN1 in blue and GluN2B in yellow) embedded in POPC lipid membrane (red and gray lines). f, The open pore (gray) obtained in simulation 3, superposed onto the closed pore of the ∆2 receptor crystal structure. Arrows indicate the transition of gate opening. g-h, MD simulation snapshots of MK-801 (g, cyan, Sim. 20) and memantine (h, orange, Sim. 24) during free-binding simulations in which they bound to the open state of the ∆2 receptor (at zero transmembrane voltage). The blockers enter the pore by the aqueous path (black arrows). MK-801 demonstrates two distributions of binding poses (cyan and yellow sticks), overlapping with MK-801 in the crystal structure (red stick) but memantine shows a predominant pose (purple). Both of them interact with asparagine residues (gray sticks) on the pore loops. i-j, Schematic representations of MK-801 and memantine binding sites, respectively. Both channel blockers induce channel closure (red arrows) while blocking the pore and adopting similar interactions with key asparagine residues.