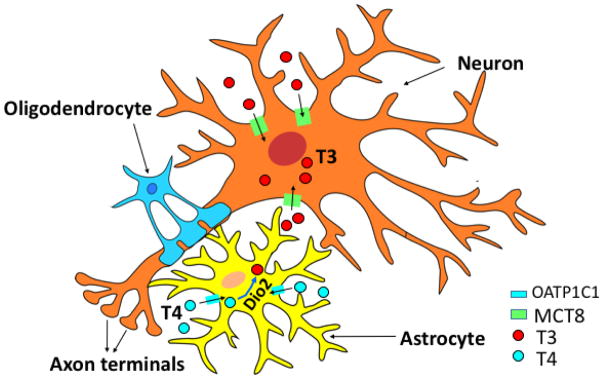
Figure 1. Model of Neurons and Glial Cells With Pathways of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism and Uptake.
Thyroid hormone action in the brain requires activation of thyroxine (T4) to the active triiodothyronine (T3), by the 5′-deiodinase 2 (Dio2), contained in glial cells. T3 uptake into neurons is mediated by specific transporters, Mct8 and Oatp1c1, present in both humans and mice, but humans appear most dependent on Mct8.