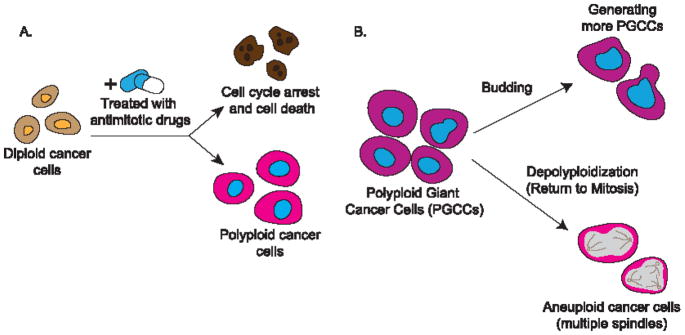
Figure 3.
Endoreplication and cancer
A. When treated with antimitotic drugs, diploid cancer cells may undergo cell cycle arrest and cell death, leading to cancer remission; they may enter endoreplication and become polyploid, fueling cancer progression. B. Polyploid giant cancer cells (PGCC) may generate progeny cells through budding; they may also undergo depolyploidization and return to mitosis, which may result in aneuploid cancer cells.