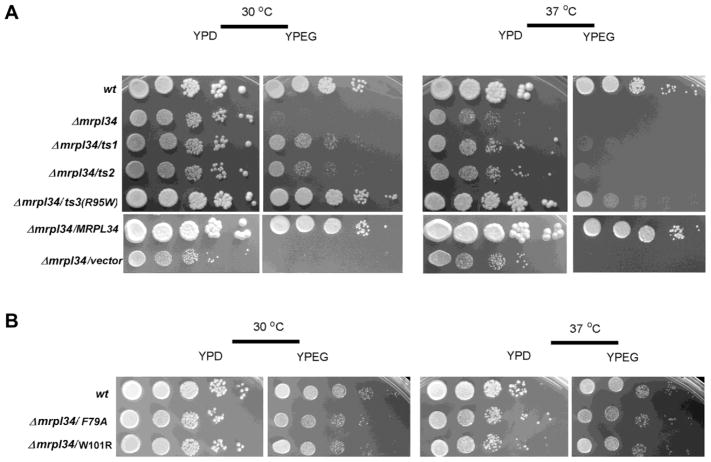
Figure 1. Growth properties of mrpl34/ts mutants.
(A) Comparative growth of wild-type cells (wt) and mrpl34 null mutant alone (Δmrpl34), or harboring plasmids expressing different mrpl34 mutants: ts alleles ts1, ts2 and ts3 (Δmrpl34/ts1, Δmrpl34/ts2, Δmrpl34/ts3(R95W) and the point mutants F79A (Δmrpl34/F79A) W101R (Δmrpl34/W101R) as well as an empty plasmid (Δmrpl34/vector) and a plasmid with the wild-type MRPL34 gene (Δmrpl34/MRPL34). Cultured cells were serially diluted and spotted in rich glucose media (YPD) and rich ethanol-glycerol media (YPEG) plates. Plates were incubated at 30° C and 37° C as indicated and photographed after three days of incubation. (B) Comparative growth of the point mutants F79A (Δmrpl34/F79A) and W101R (Δmrpl34/W101R) was also performed as in “A”.