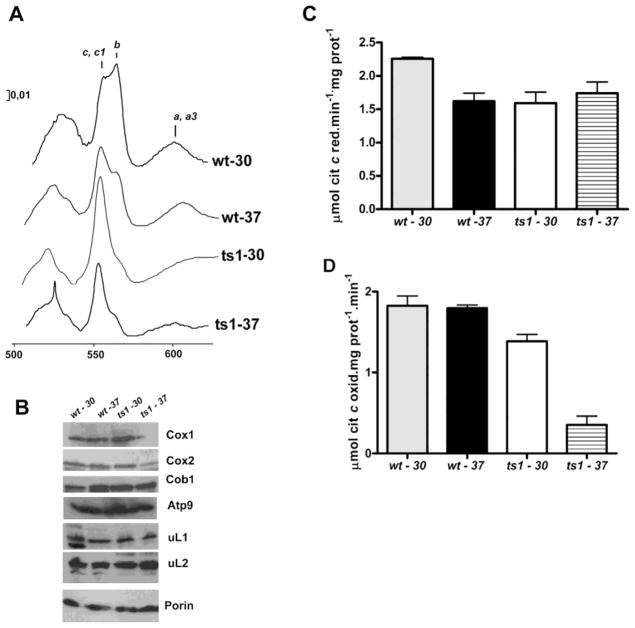
Figure 4. Respiratory properties of bL34 ts1 mutant.
(A) Mitochondria were isolated from the respiratory competent parental strain W303-1B (wt) and from the Δmrpl34/ts1 mutant (ts1) grown in rich 2% galactose media at 30° C and 37° C as indicated. (YPGal). The mitochondria were extracted at a protein concentration of 5 mg/ml in the presence of 1% potassium deoxycholate and 1 M KCl. The spectra of the extracts were obtained at room temperature following oxidation of the sample in the reference cuvette with potassium ferricyanide and reduction of the sample cuvette with sodium dithionite. The α absorption bands corresponding to cytochromes c, c1, b, a, and a3 are indicated. (B) Mitochondrial proteins from wild-type (wt) and Δmrpl34/ts1 (ts1) were also separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and were reacted with antibodies against the respective antibodies indicated on the right side of the panel. The blots were then treated either with peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse, or anti-rabbit IgG. The proteins were visualized based on luminol-H2O2 peroxidase chemiluminescence system and intensified with r-coumaric acid. (C) NADH cytochrome c reductase activity in mitochondria isolated as in “A” (D)′ Cytochrome c oxidase activity; the bars in “B” and “C” represent the specific activity obtained in four different measurements from two different mitochondrial preparations.