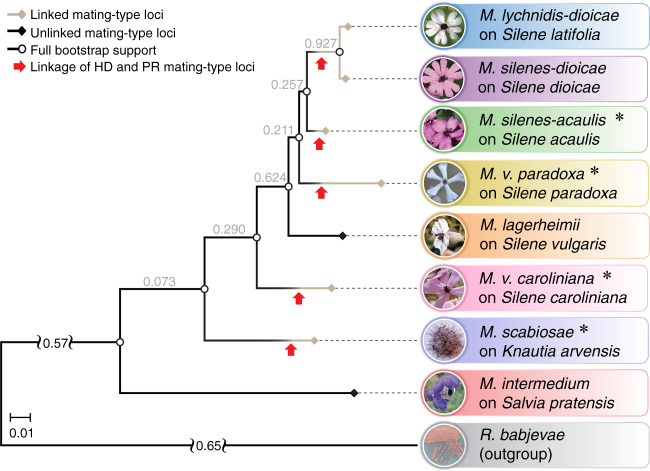
Fig. 1.
Phylogenies of anther-smut fungi and their breeding systems. Phylogenetic tree of the studied Microbotryum species (shown in the anthers of their host plants) and the outgroup Rhodotorula babjevae, based on 4229 orthologous genes. Species whose genomes were obtained in the present study are indicated by asterisks. Branch color and symbol indicate linked (gray branches and diamonds) or unlinked (black branches and diamonds) mating-type loci. The white circles indicate full bootstrap support. Red arrows indicate independent mating-type locus linkage events. Tree internode certainty with no conflict bipartitions (the normalized frequency of the most frequent bipartition across gene genealogies relative to the summed frequencies of the two most frequent bipartitions) is provided below the branches, indicating good support for the nodes. Relative certainty for this tree is 0.397